GALLERY OF FOREST SPECIES CONNECTED WITH HABITAT TREES
Original, hand-made illustrations of forest species were created directly for the Department of Forest Ecology FFWS, CULS as part of the Forest Diversity project and will be continuously updated for you.

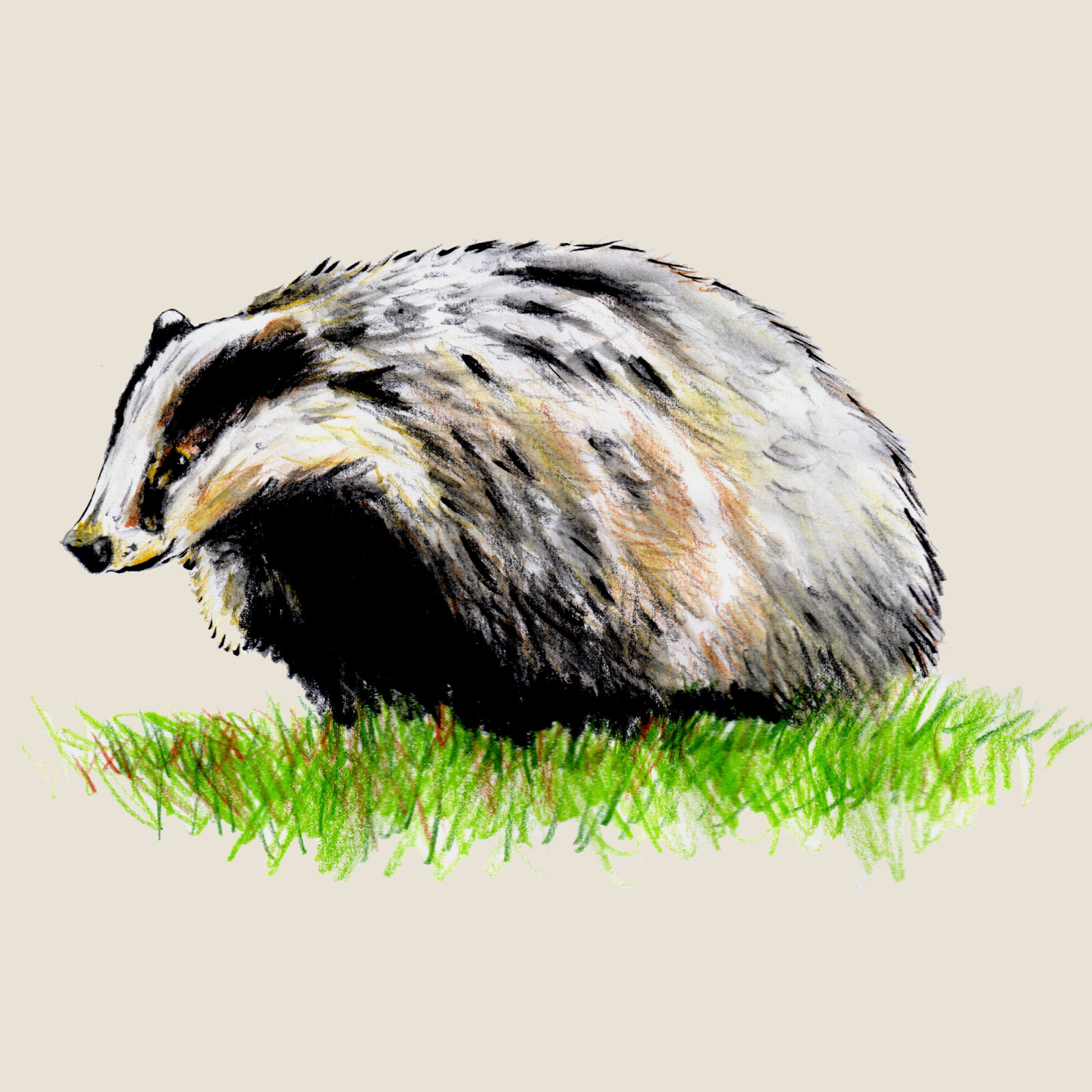
European badger
(Meles meles)Code: 5
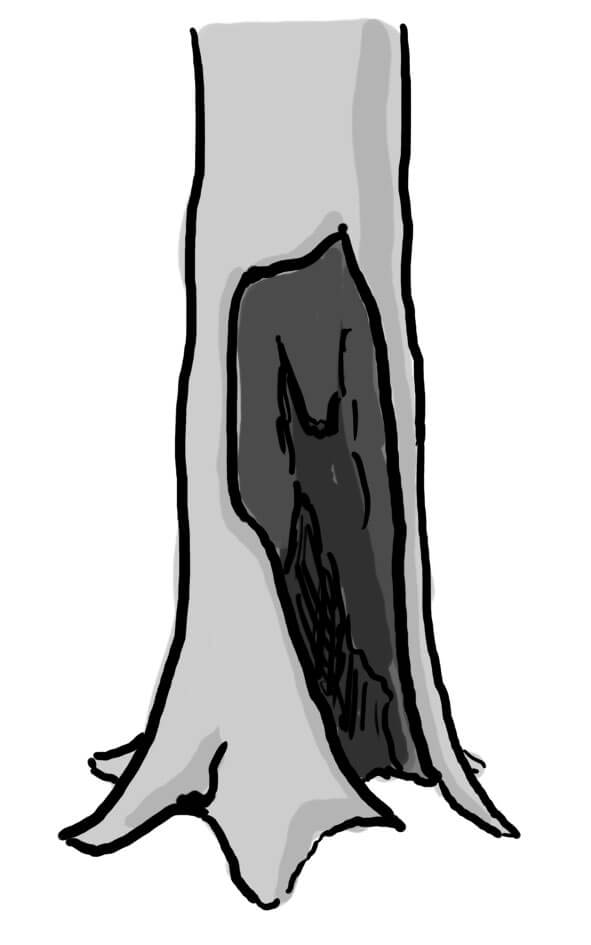
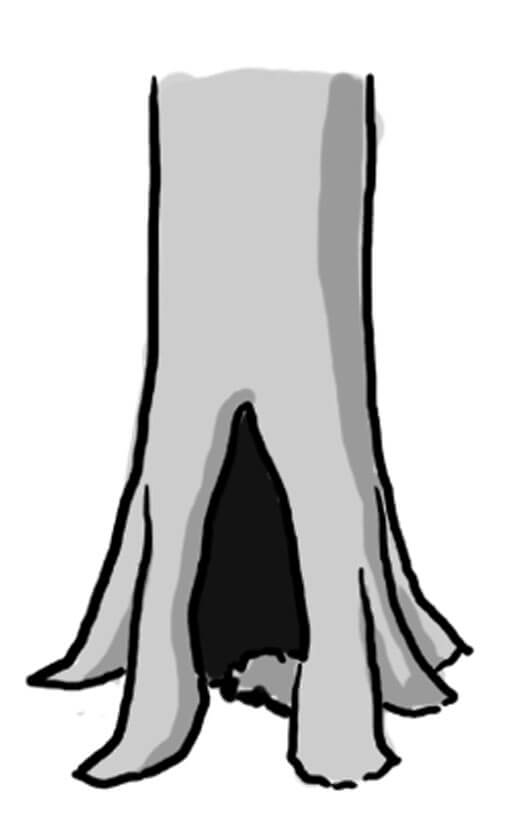
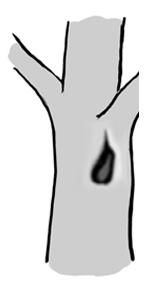
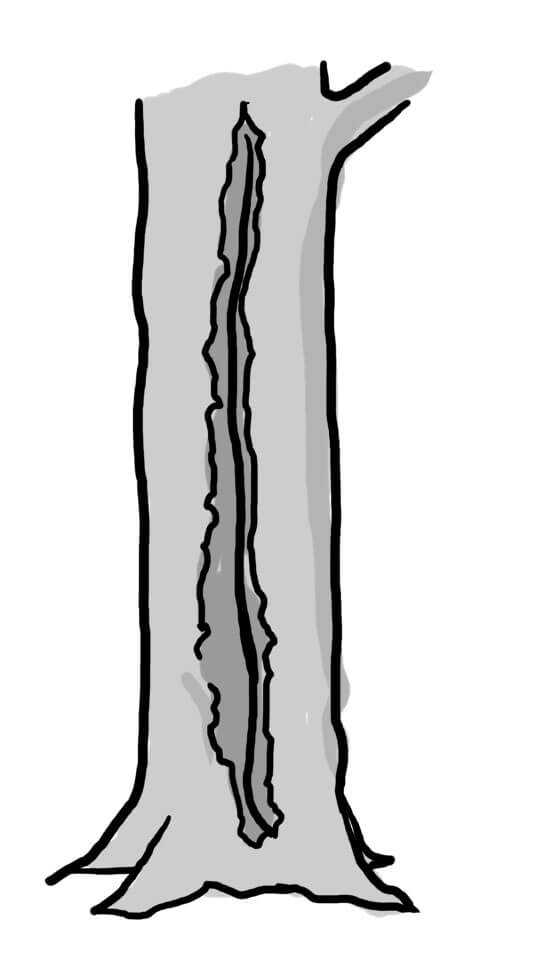
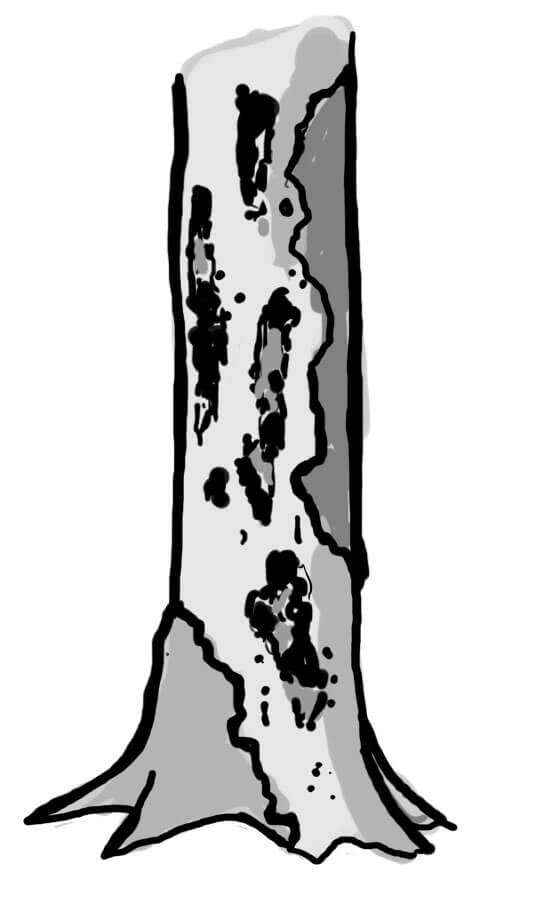
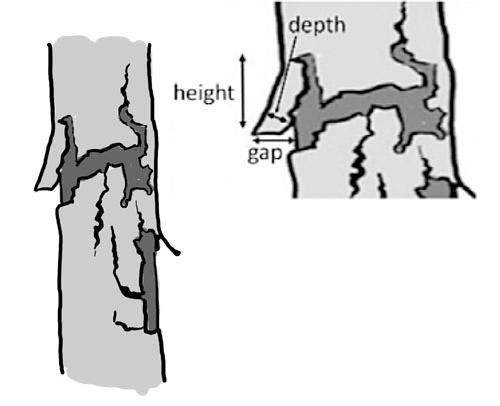
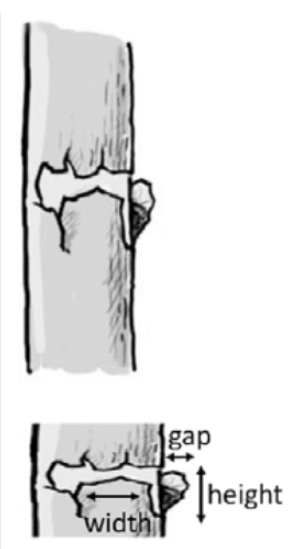
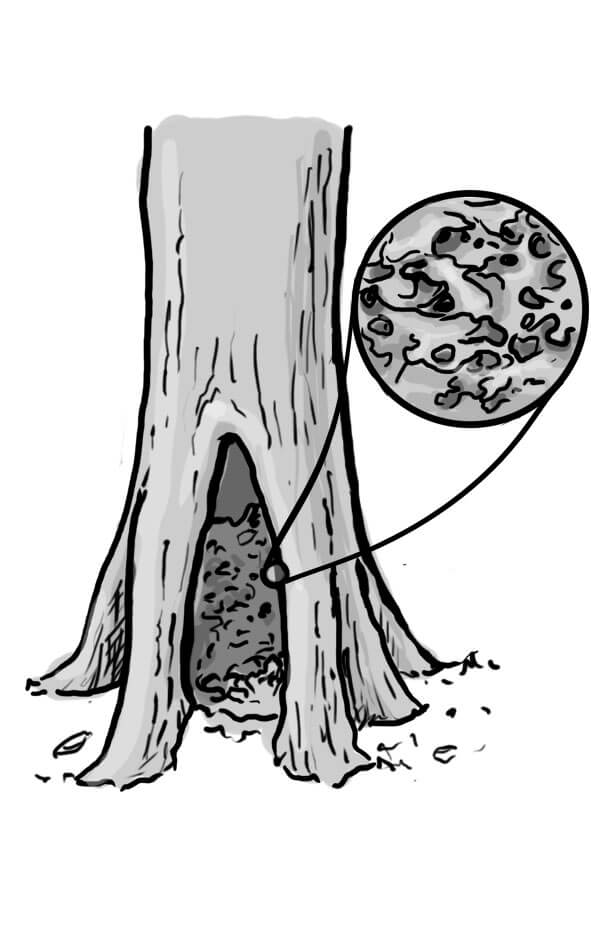
Trunk base rot-hole (closed top, ground contact)
Type
Opening ø > 10 cm
Description
Cavity chamber is completely protected from surrounding microclimate and rain Top-closed trunk cavity containing more or less mould (depending on its development stage). The cavity bottom has ground contact. Note that the cavity entrance can be higher on the trunk. Countable.

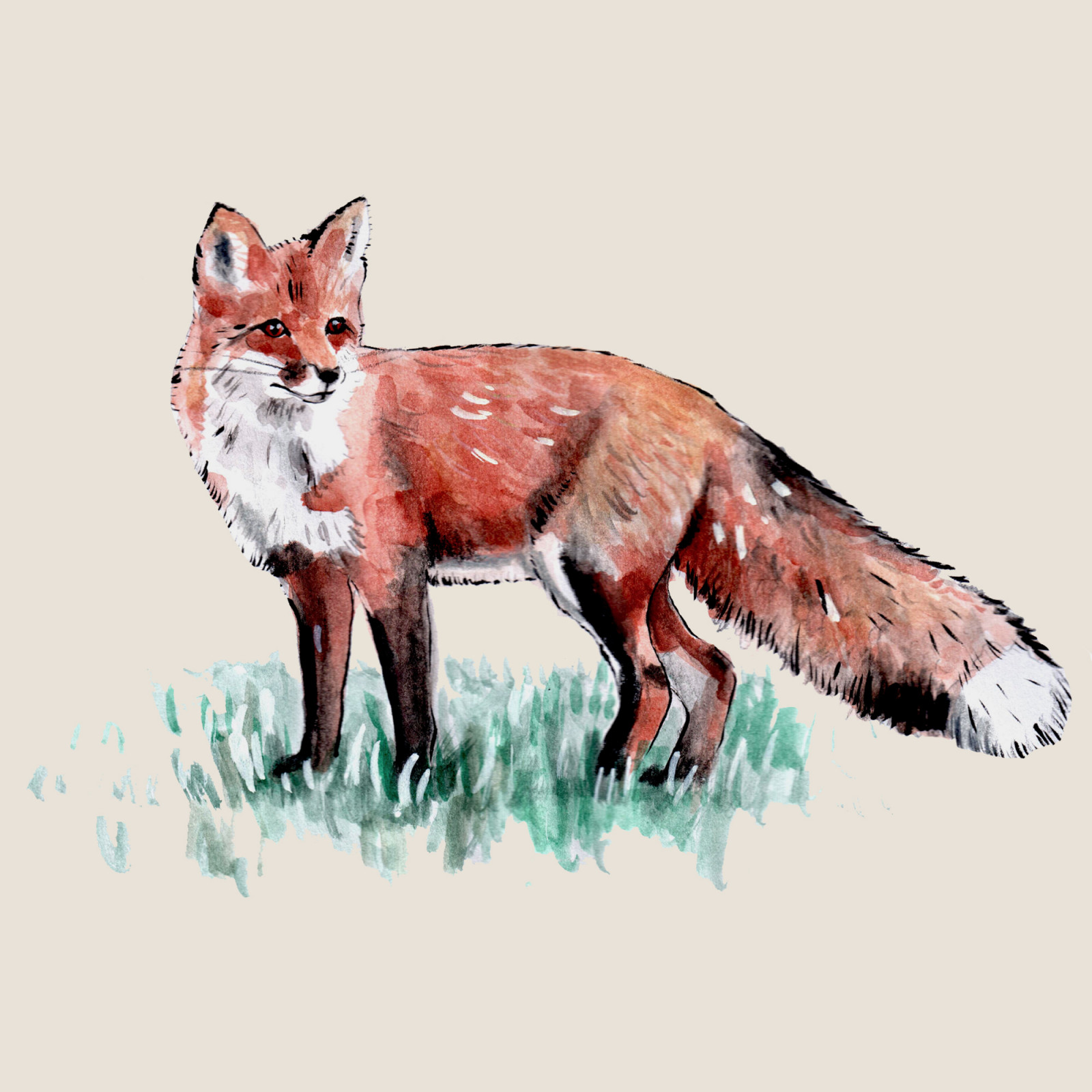
Red fox
(Vulpes vulpes)Code: 5
Trunk base rot-hole (closed top, ground contact)
Type
Opening ø > 10 cm
Description
Cavity chamber is completely protected from surrounding microclimate and rain Top-closed trunk cavity containing more or less mould (depending on its development stage). The cavity bottom has ground contact. Note that the cavity entrance can be higher on the trunk. Countable.
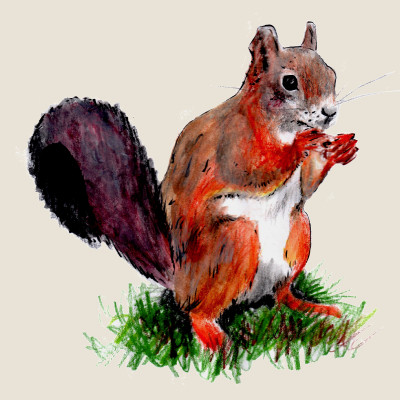

Red squirrel
(Sciurus vulgaris)Red squirrel (Sciurus vulgaris)
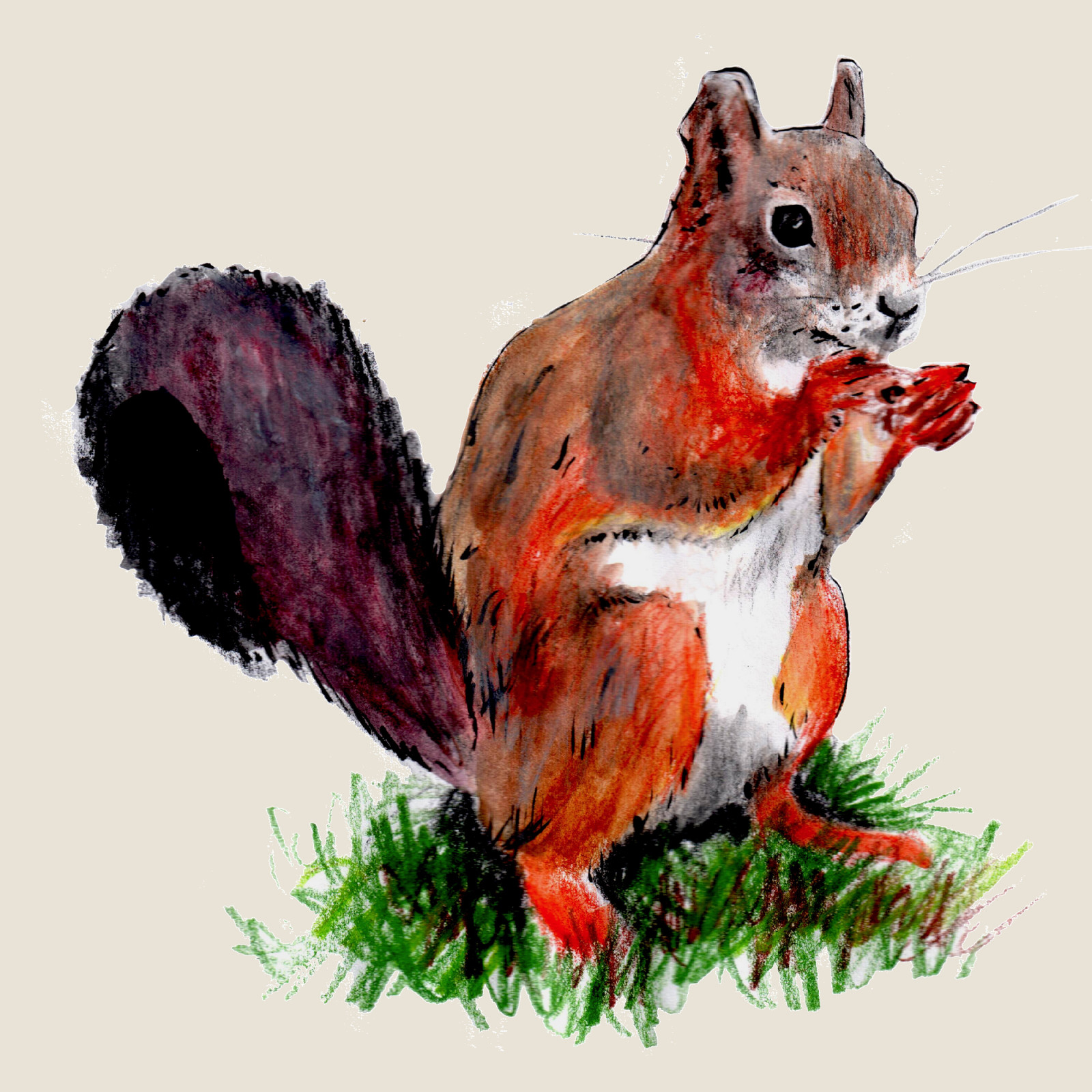

The red squirrel, i.e. a medium-sized rodent from the squirrel family, can be seen in all types of forests, parks, alleys and gardens in the Czech Republic. A characteristic feature of the red squirrel, which in our territory normally abounds in black, brown or even red, are tufts of hair on the earlobes pointing to the tip. Except for the breeding season, squirrels live a solitary way of life, which they spend outside the time of searching for food mainly in tree cavities or nests on stronger branches. Lives mainly on seeds of pine cones, nuts and dried mushrooms and fruits.
Tree microhabitats associated with me
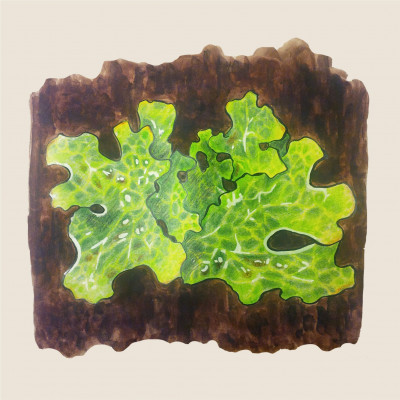

Tree lungwort
(Lobaria pulmonaria)Tree lungwort (Lobaria pulmonaria)

The Tree lungwort is found mainly in old primary forests, where it prefers moss-covered beech trees. This epiphytic (growing on living plants, but feeding on its own), the largest lichen in the Czech Republic, is sensitive to polluted air and precisely because of high emissions and the intensification of forestry in the second half of the 20th century, it began to retreat from the Czech Republic. Of the majority of mountain and foothill areas where it used to be common, today it can only be found in a few locations, such as the Šumava Mountains. From the point of view of nature protection, it is a flagship species in the Czech Republic.
Tree microhabitats associated with me
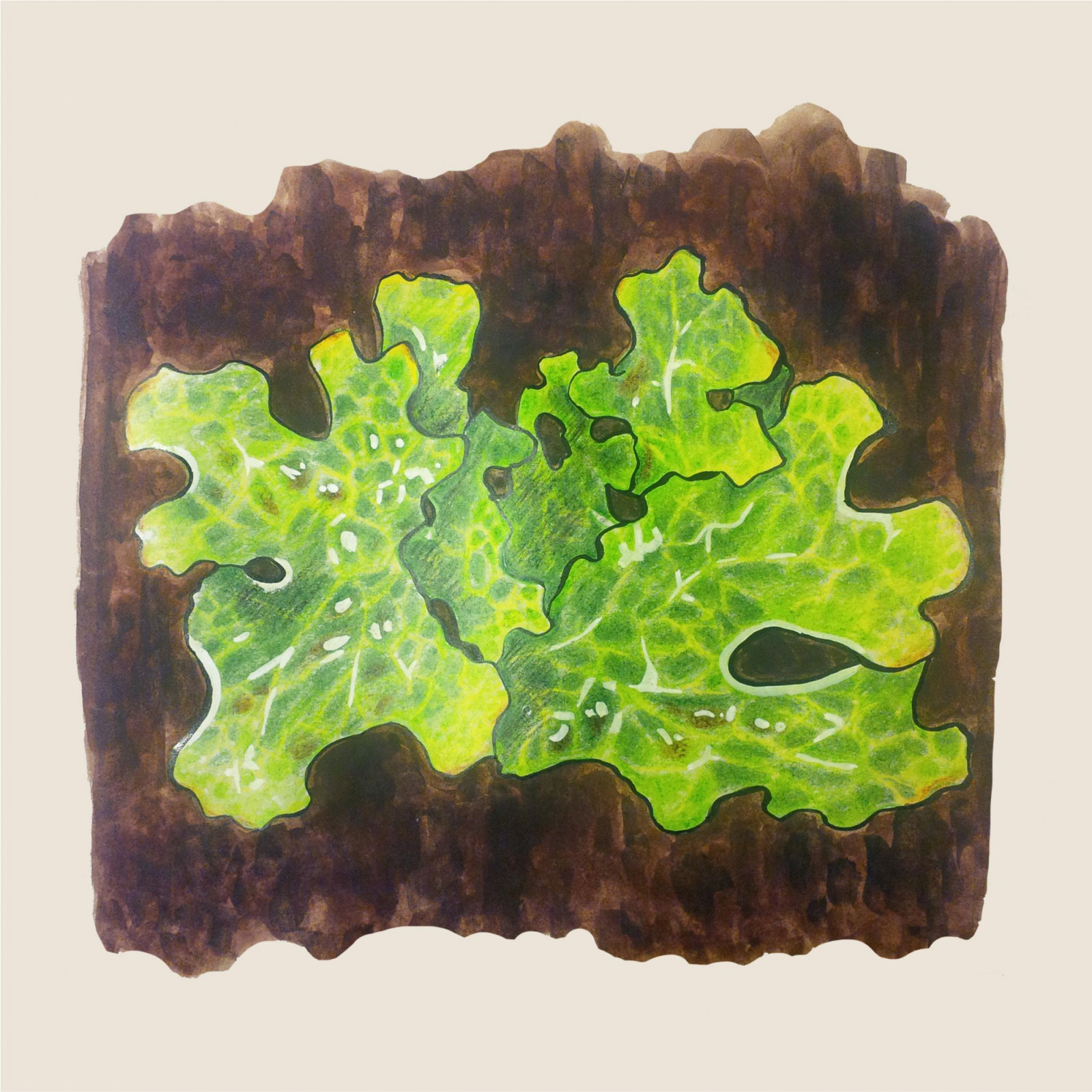
Beard moss
(Usnea barbata)Beard moss (Usnea barbata)

The Beard Moss is an epiphytic (growing on living plants but feeding on its own) lichen, which is characterized by an overhanging rhizome with irregularly thick branches and thin bark. In the Czech Republic, this is one of the most common species of beard lichens. Since the second half of the 20th century, mainly due to acid rain, the occurrence of Beard Moss has decreased significantly. However, after the improvement of air quality at the beginning of the new millennium, it spread again and nowadays it can be found quite often all over the territory of the Czech Republic.
Tree microhabitats associated with me
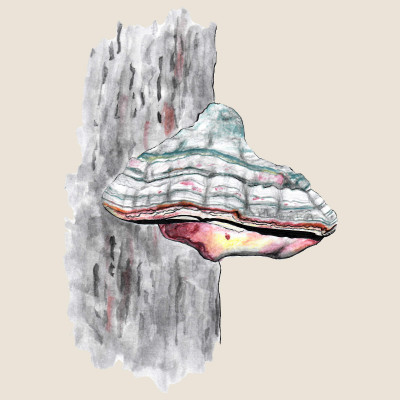

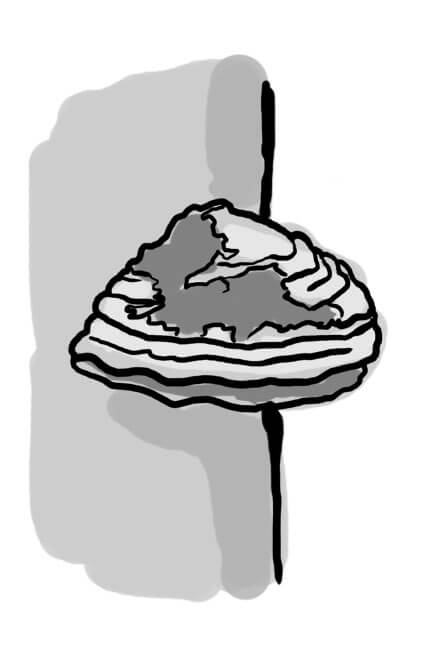
Hoof fungus
(Fomes fomentarius)Hoof fungus (Fomes fomentarius)
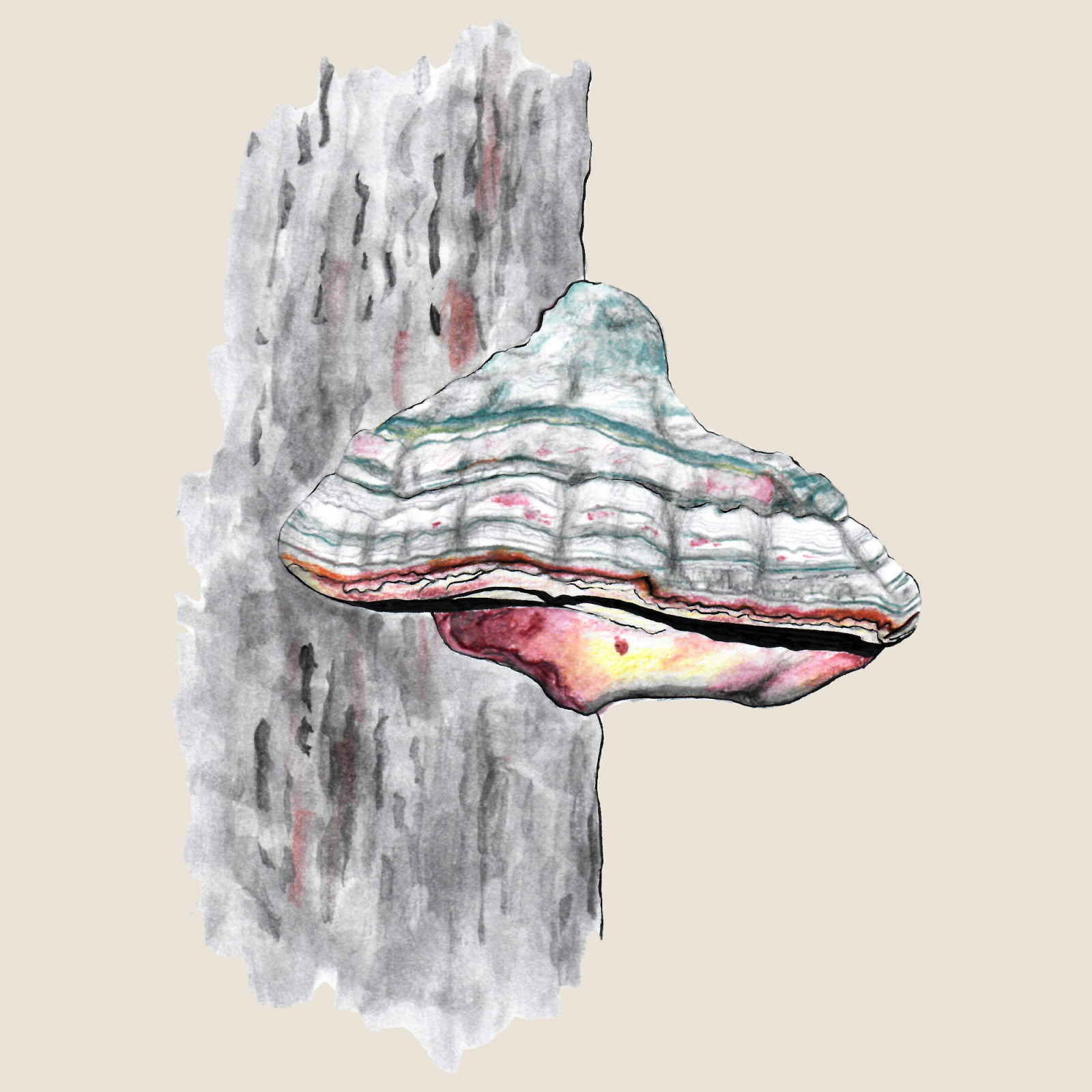

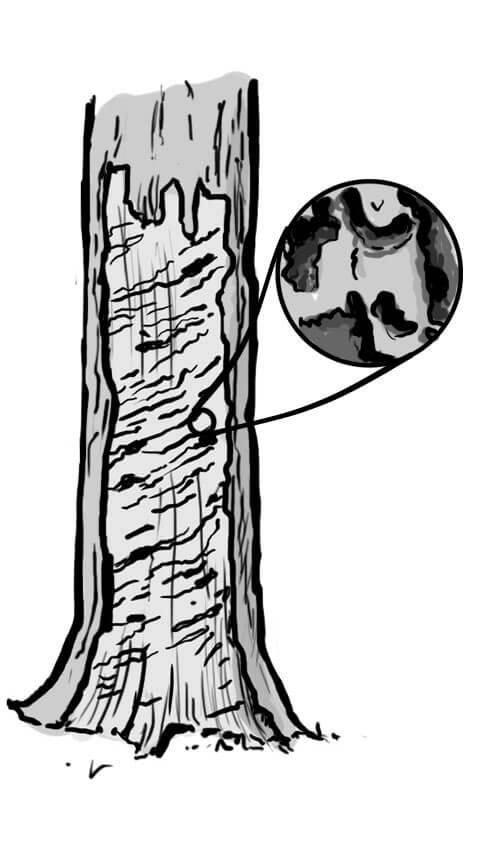
The Hoof Fungus is a perennial, wood-decaying, inedible fungus from the Polyporaceae family. The fruiting body of this mushroom, which can reach up to 50 cm in width and up to 25 cm in length, has a hoof-like shape. Its surface is covered with a hard, matte bark that changes color depending on age. The Hoof Fungus laterally grows to the trunks or strong branches of living and dead trees, where it can survive for up to 30 years. It occurs abundantly from the lowlands to the mountains mainly on deciduous trees, especially beech and birch. It is rarely found on coniferous tree species. Because it decomposes wood, it belongs to the decomposers.
Tree microhabitats associated with me
Code: 32
Perennial polypore
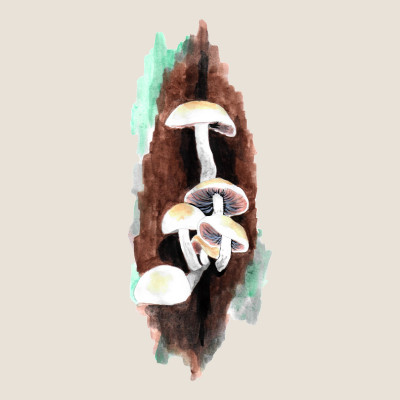
Psathyrella cernua
(Psathyrella cernua)Psathyrella cernua (Psathyrella cernua)
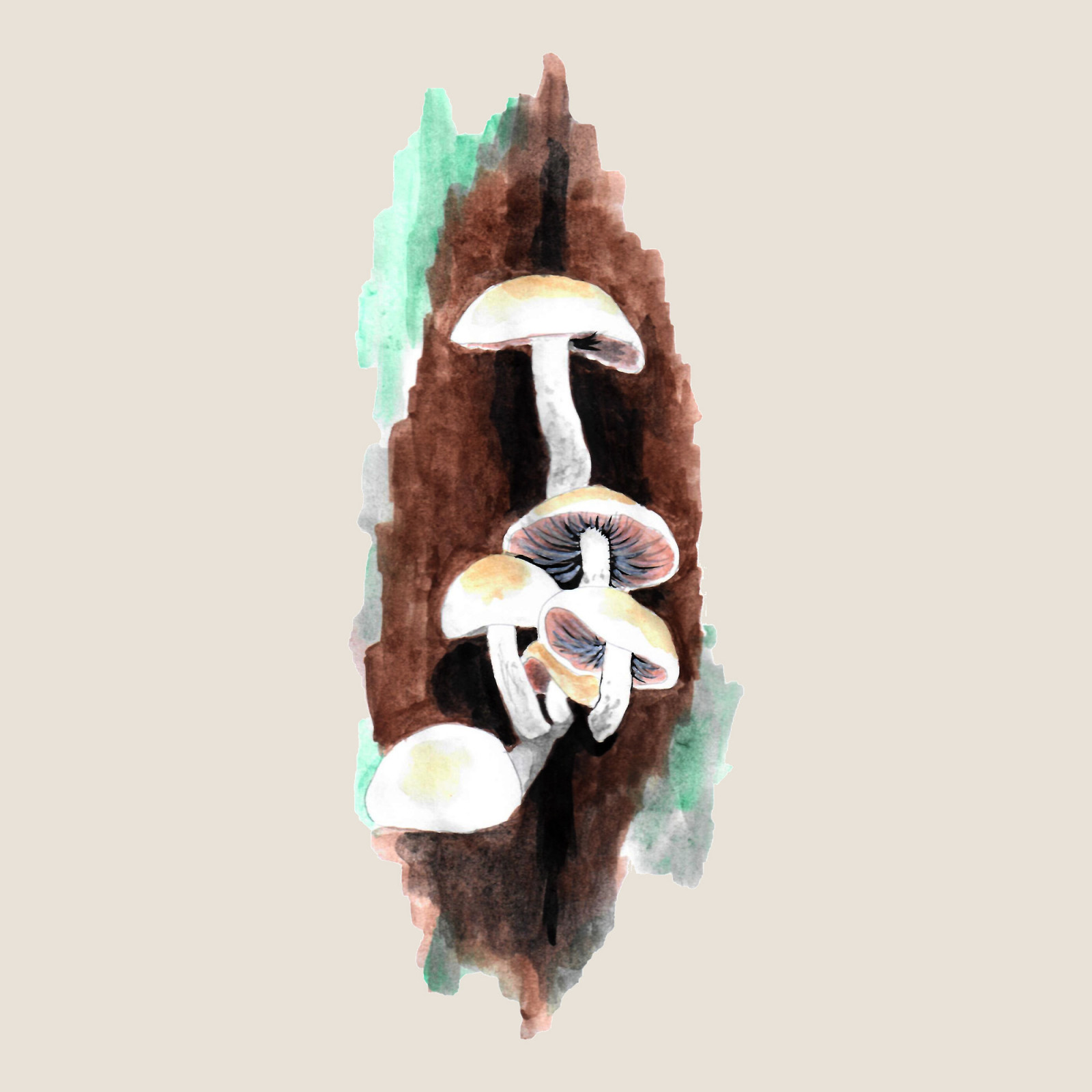
Psathyrella cernua is a fungus that forms medium-sized fruiting bodies growing in bunches. They often grow at the base of the trunks or in the hollows of deciduous trees - mainly beech and maple, less often also on lindens, poplars, alders or elms. We can also find this fungus on fallen trees or stumps in deciduous and mixed natural forests.
Tree microhabitats associated with me
Code: 5
Trunk base rot-hole (closed top, ground contact)
Type
Opening ø > 10 cm
Description
Cavity chamber is completely protected from surrounding microclimate and rain Top-closed trunk cavity containing more or less mould (depending on its development stage). The cavity bottom has ground contact. Note that the cavity entrance can be higher on the trunk. Countable.
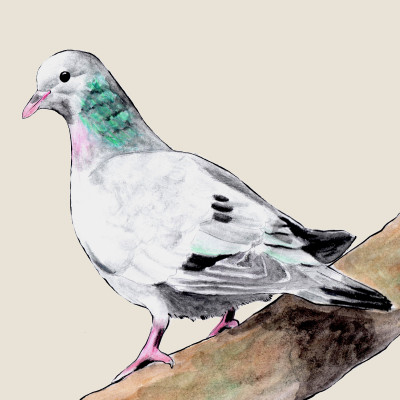

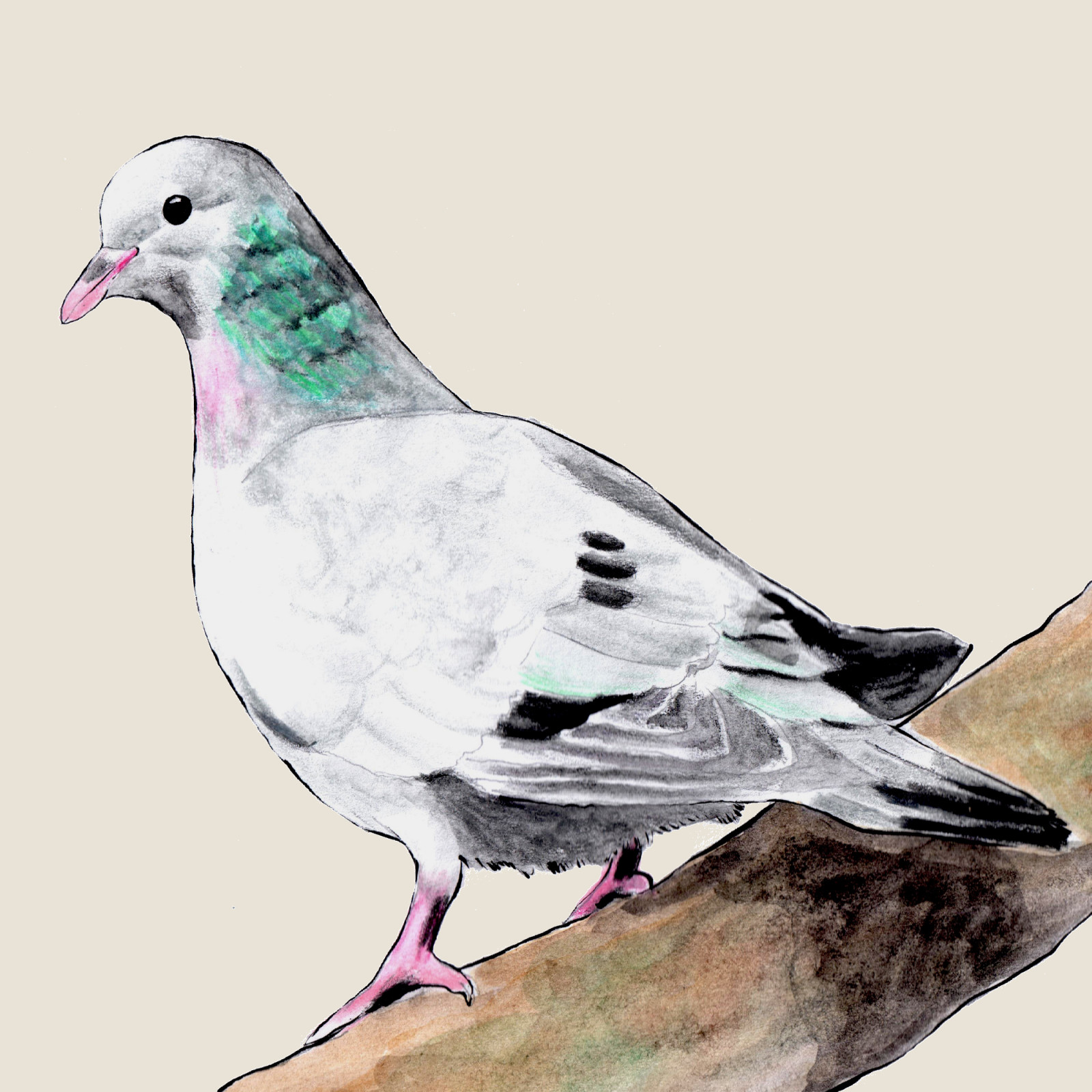
Stock dove
(Columba oenas)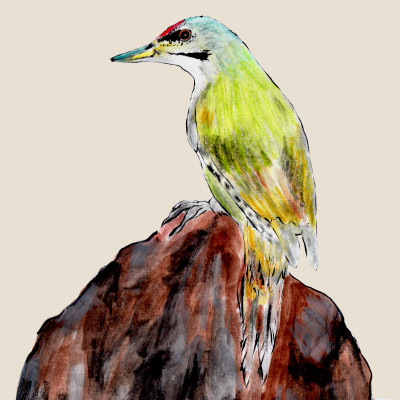
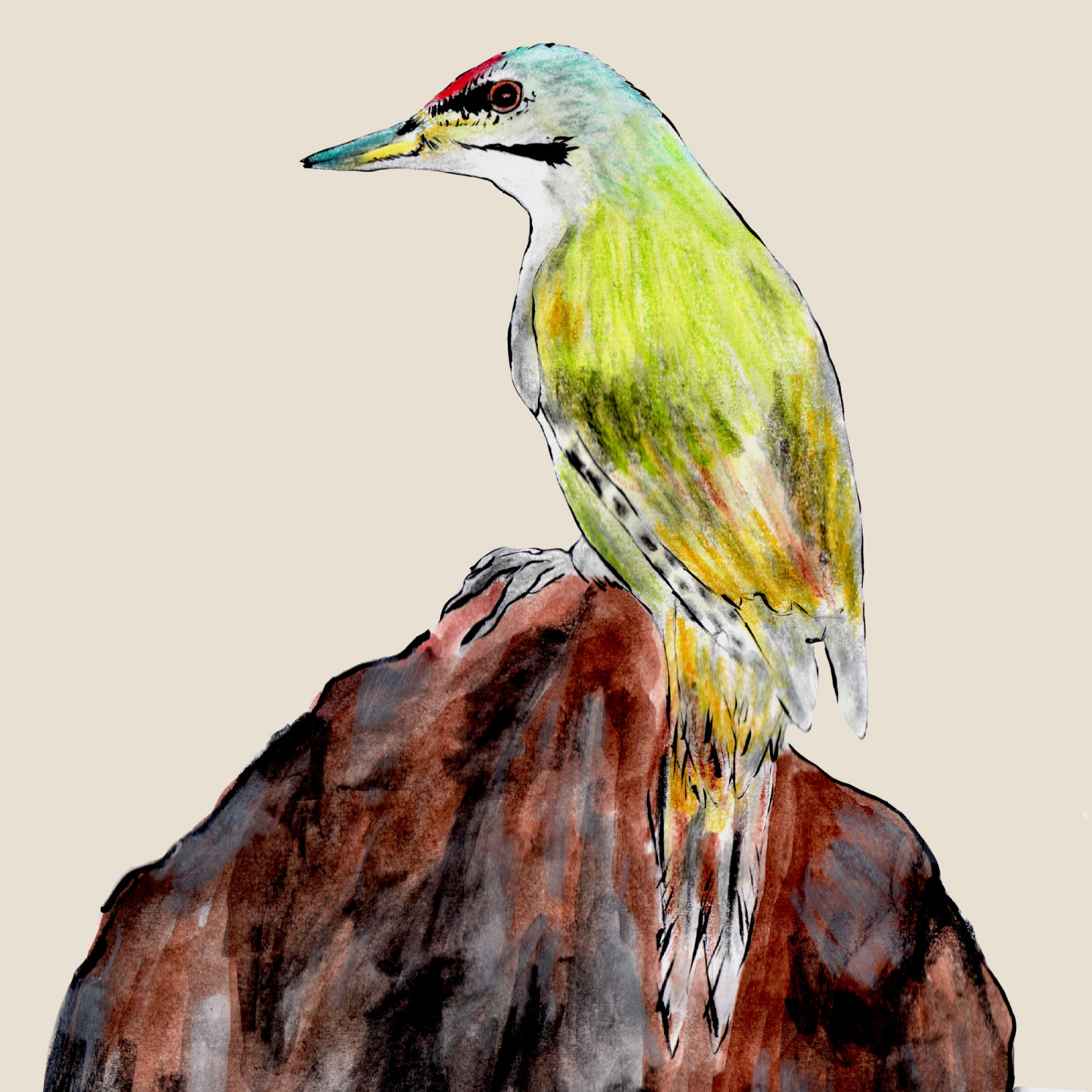
Grey-headed Woodpecker
(Picus canus)
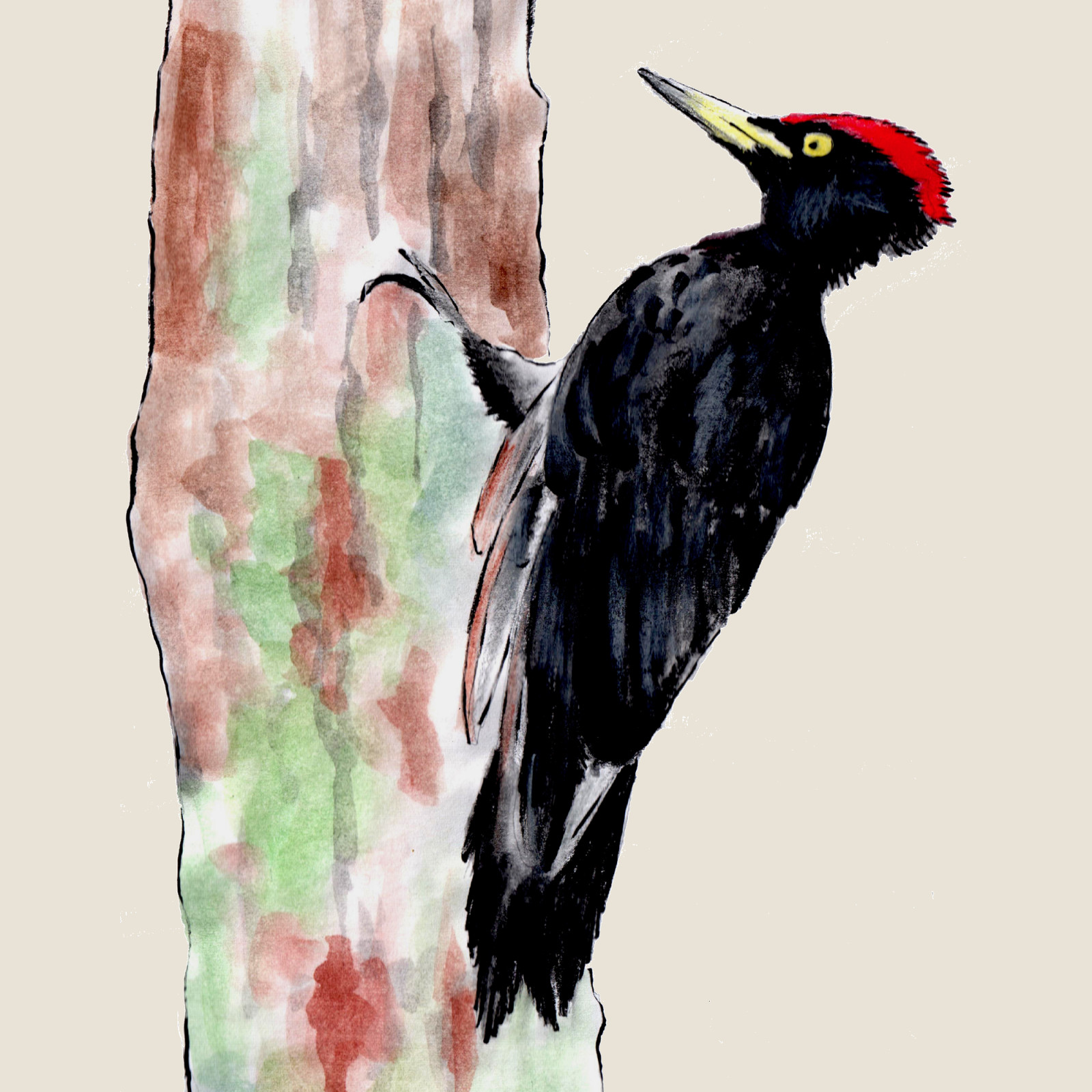
Black Woodpecker
(Dryocopus martius)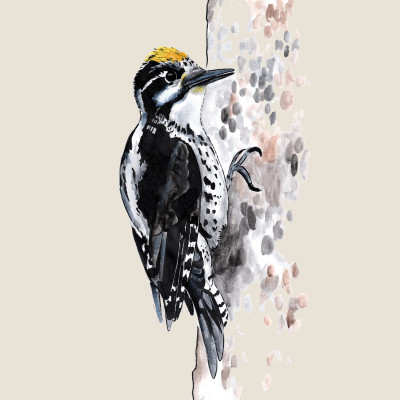
Three-toed woodpecker
(Picoides tridactylus)Three-toed woodpecker (Picoides tridactylus)
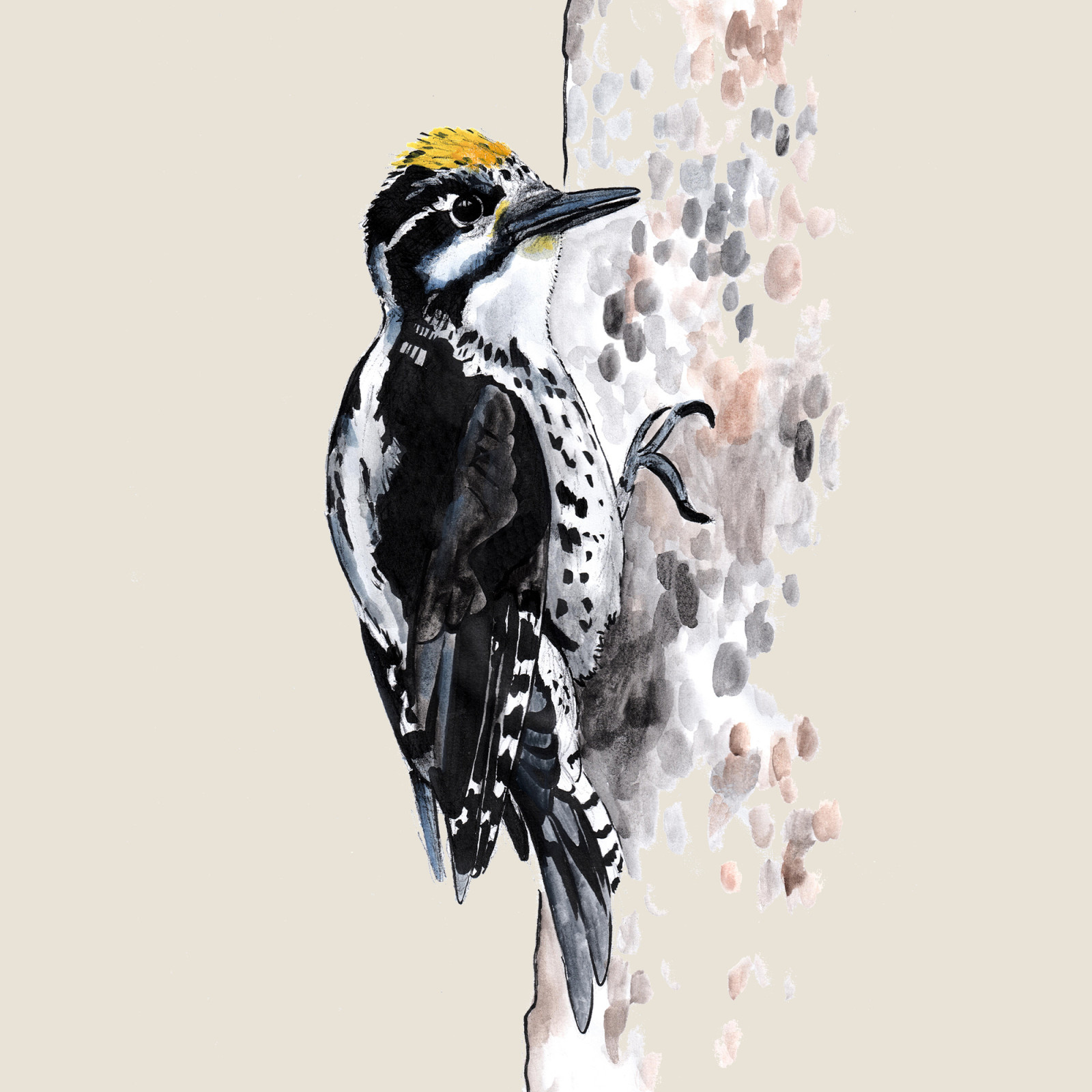

The Three-Toed Woodpecker is a shy, medium-sized, white-and-black species of woodpecker with two broad stripes on its cheek. Males have a yellow crown on their head, while females have a black crown. Overall, its coloration is similar to that of a white-backed woodpecker, but without the red feathers. It occurs in old coniferous and mixed forests, preferring spruce stands with a large amount of dead trees. Its food consists mainly of invertebrates, which it searches for under the bark, but he does not disdain the oozing resin either.
Tree microhabitats associated with me

White-backed woodpecker
(Dendrocopos leucotos)White-backed woodpecker (Dendrocopos leucotos)
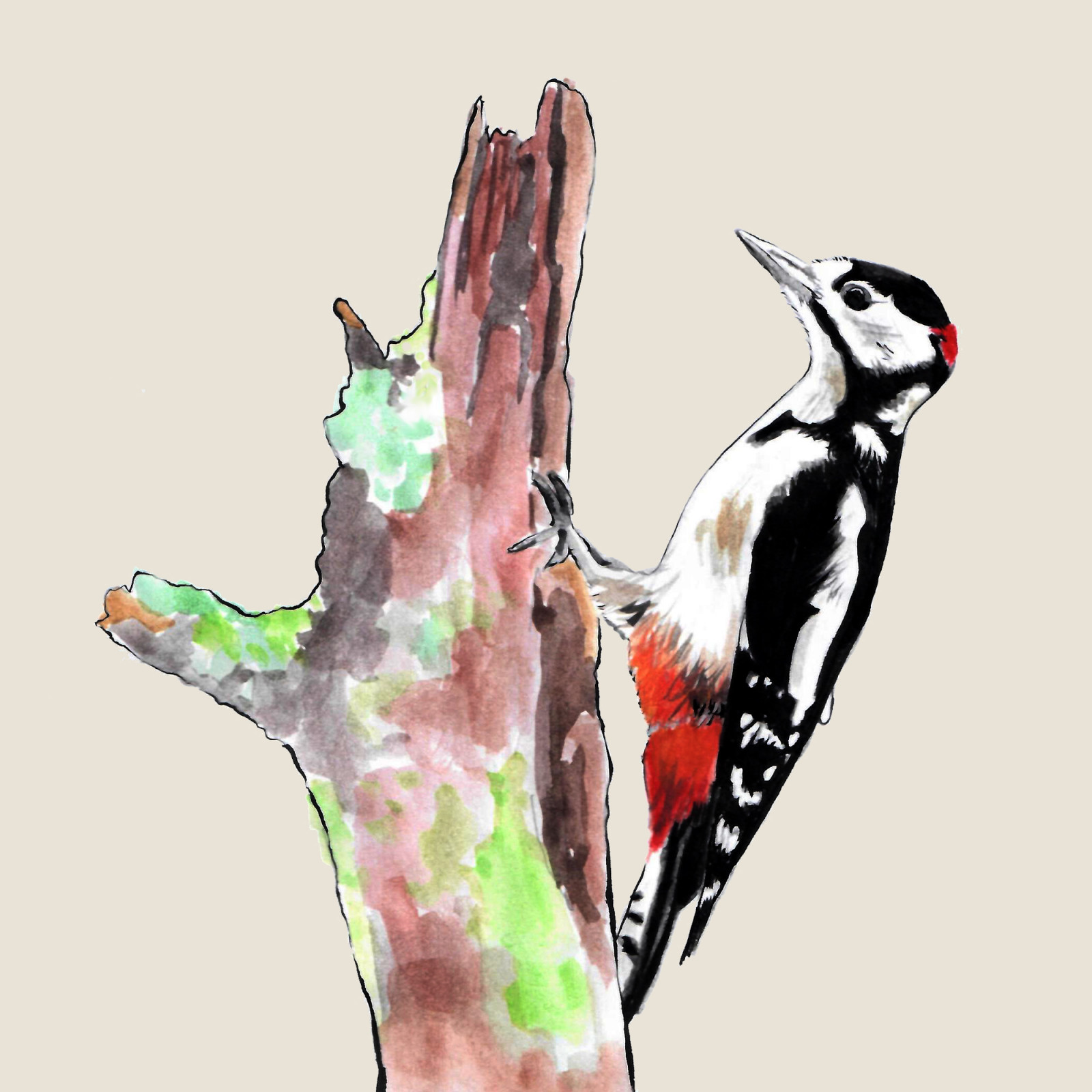

The White-Backed Woodpecker is a large climber with a long beak. Its white back is not always obvious, but clearly visible during flight. It has distinctive striped flanks and red feathers on the underbelly and tail. The woodpecker prefers older stands of deciduous and mixed forests with lots of dead trees. Unfortunately, it is currently threatened by the loss of suitable habitats, i.e. the lack of surviving and dead trees of large dimensions.
Tree microhabitats associated with me
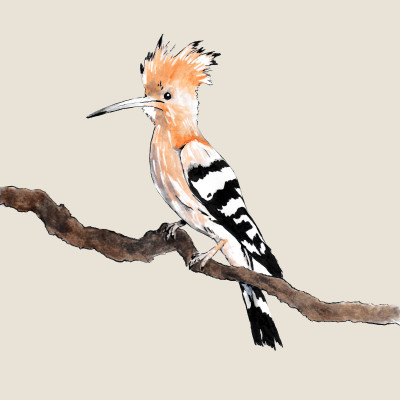

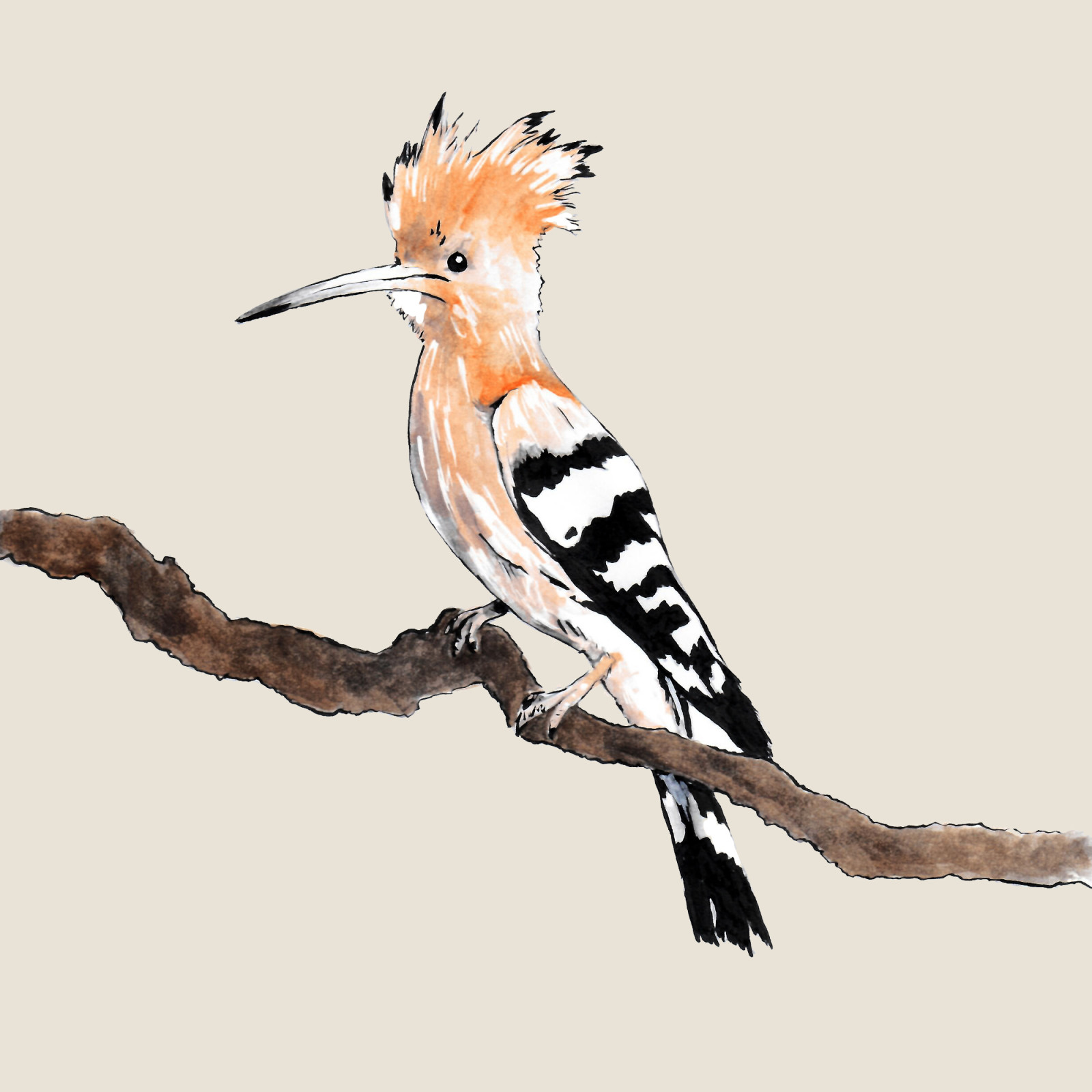
Eurasian hoopoe
(Upupa epops)
Tawny owl
(Strix aluco)Tawny owl (Strix aluco)
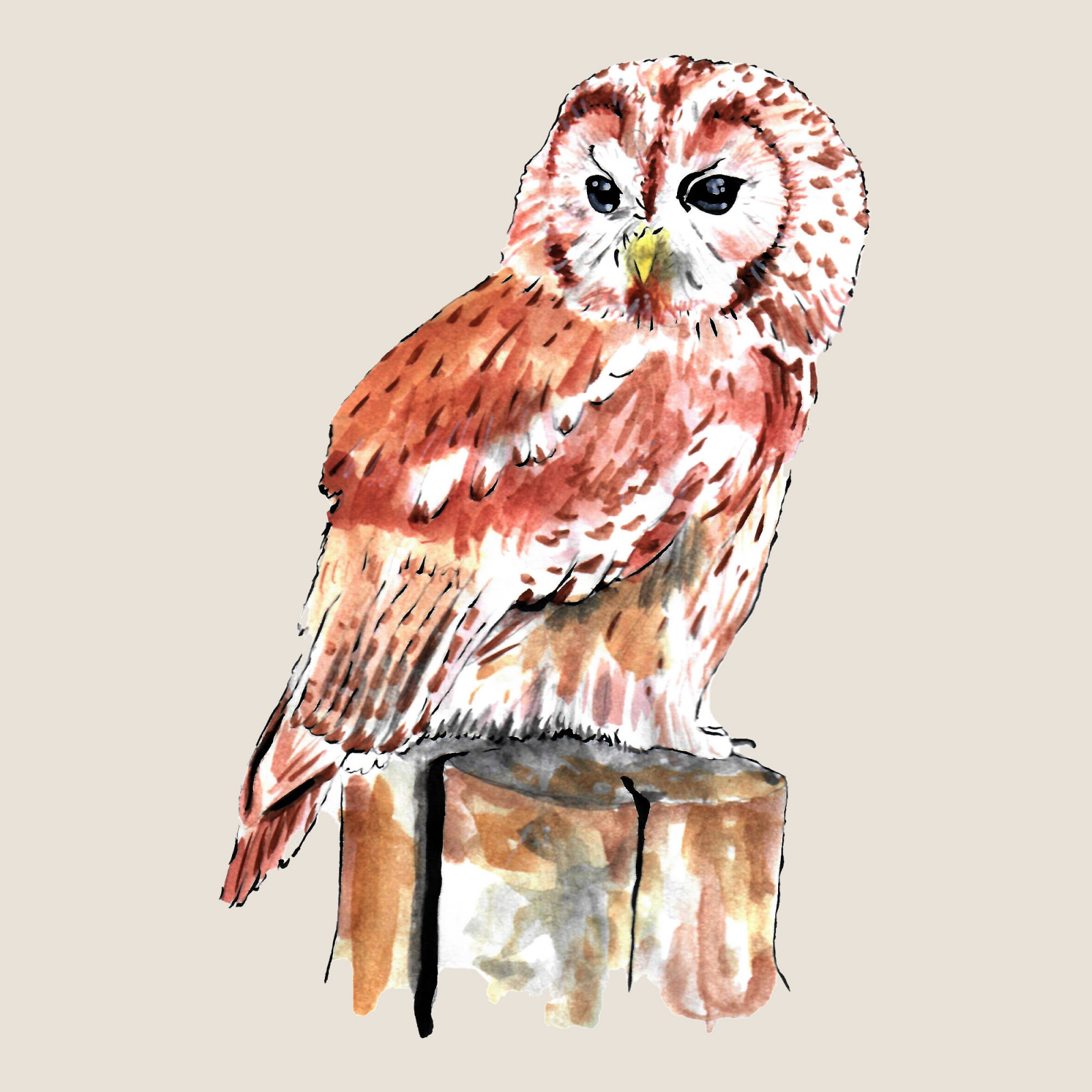

Tawny owl is the most numerous owl in the Czech Republic. It inhabits deciduous and mixed forests, but it can also be found in city parks, groves or moors. It is active at night and its food consists mainly of rodents, birds, but also insects and fish. Nests in tree hollows and rarely also on nests of other birds (especially raptors).
Tree microhabitats associated with me
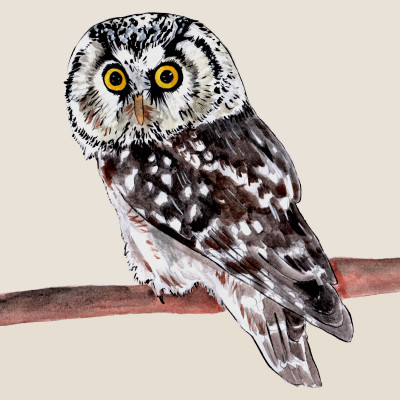

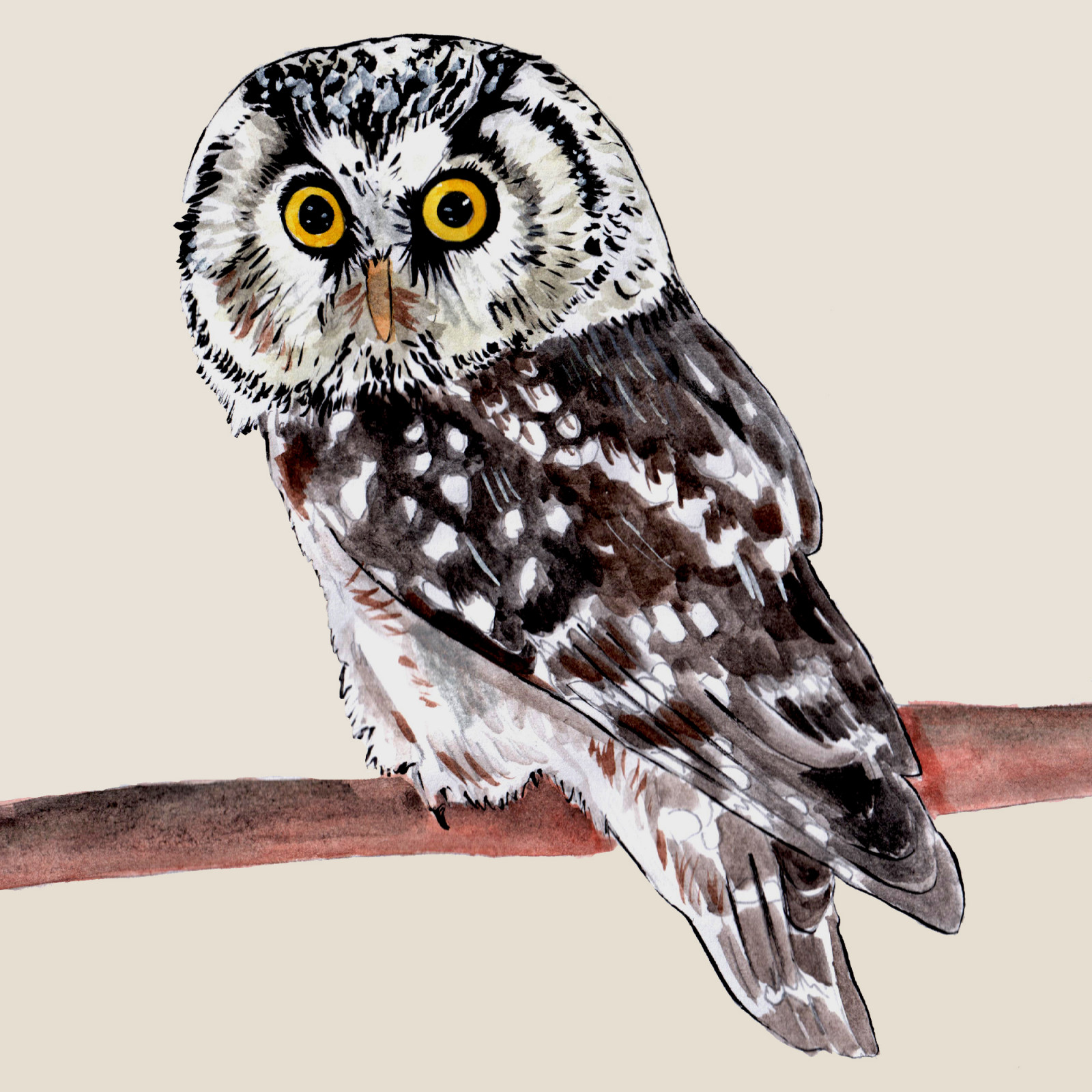
Boreal Owl
(Aegolius funereus)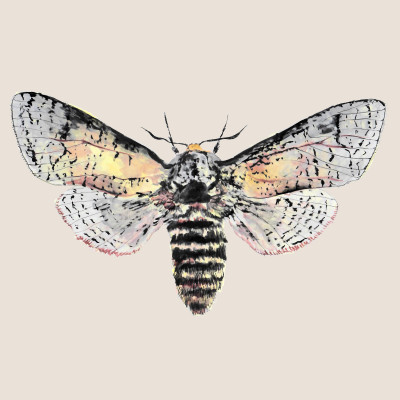
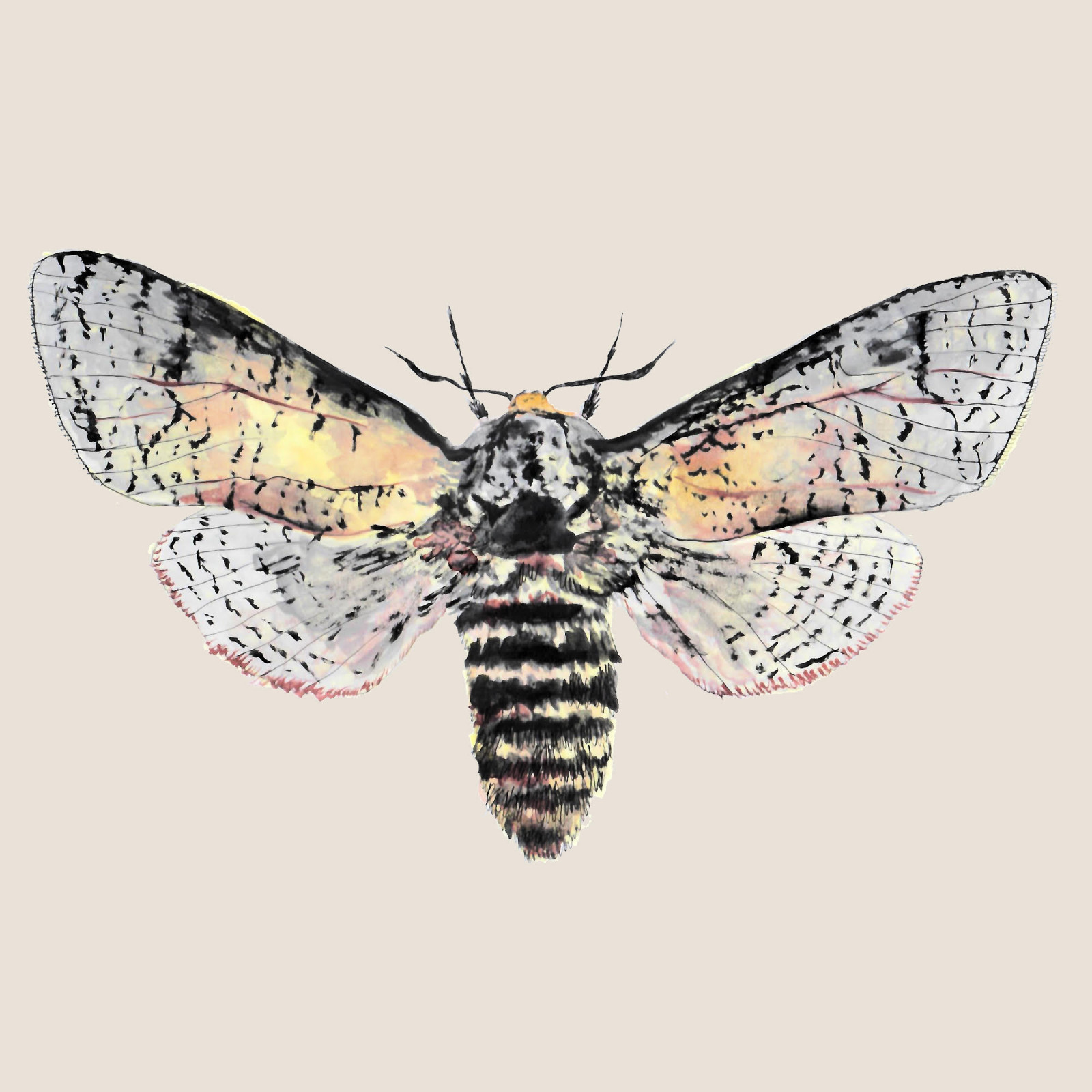
Goat moth
(Cossus cossus)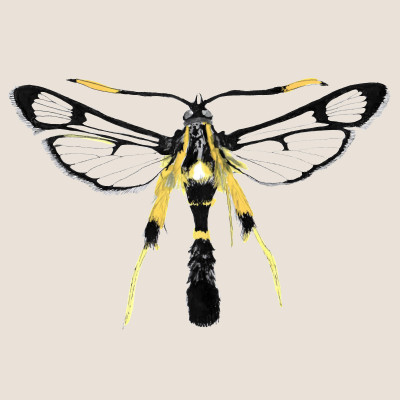
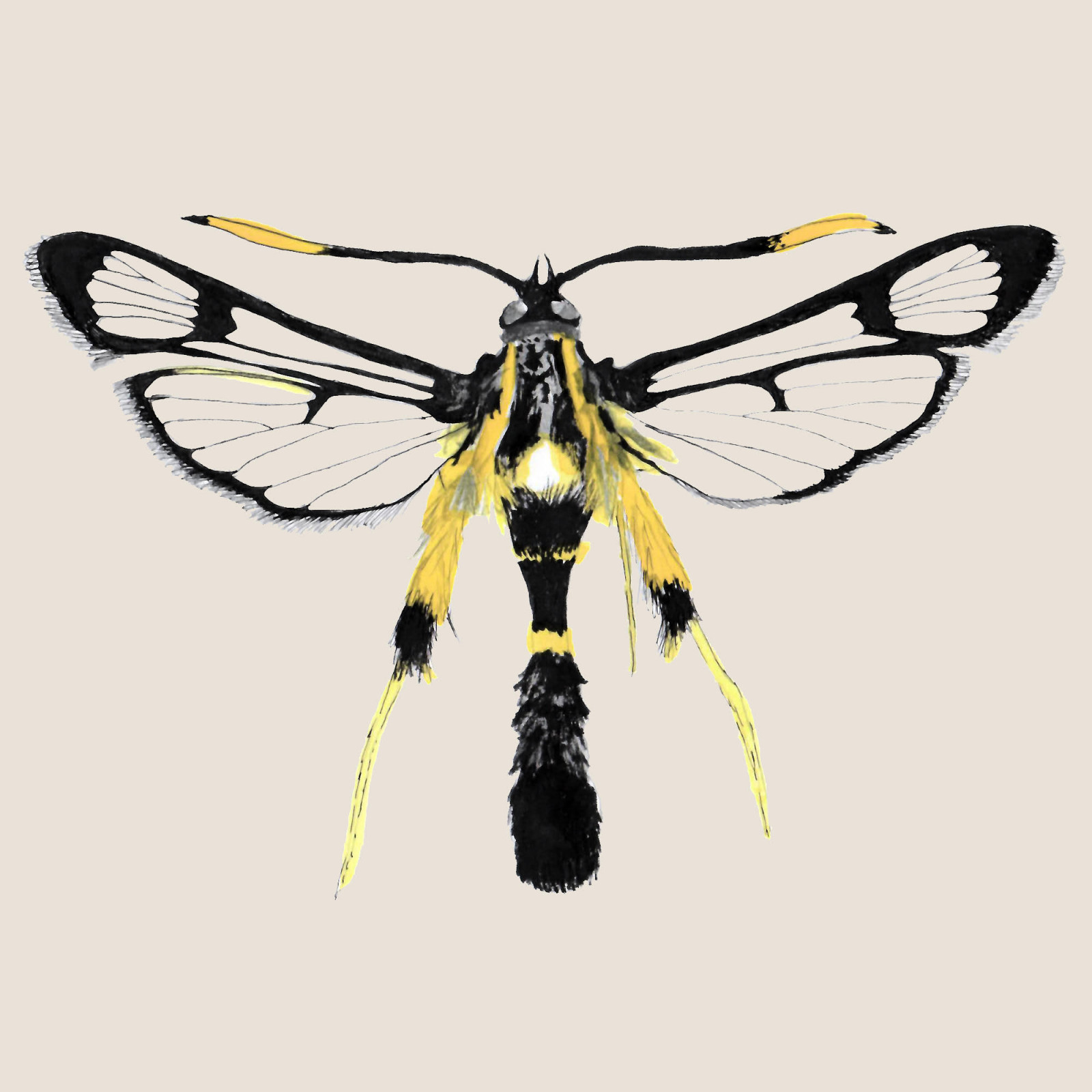
Synanthedon mesiaeformis
(Synanthedon mesiaeformis)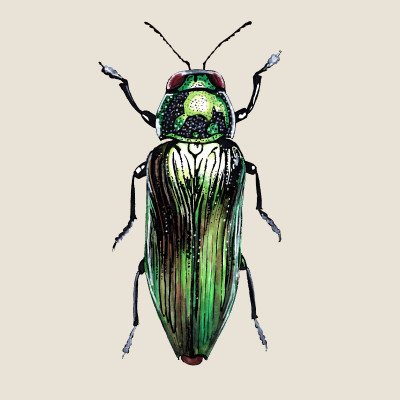
Oak Jewel Beetle
(Eurythyrea quercus)Oak Jewel Beetle (Eurythyrea quercus)
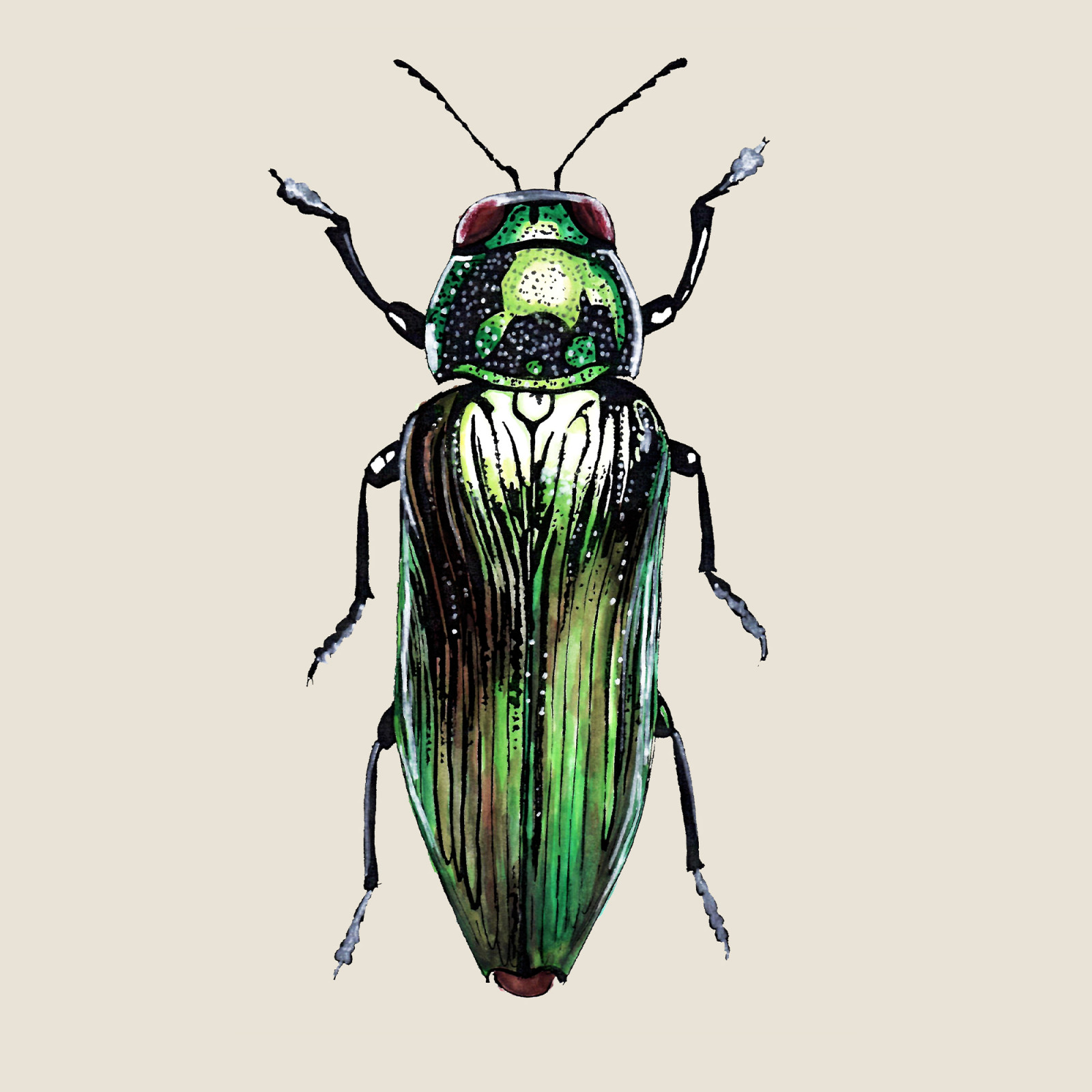

The Oak Jewel Beetle is a shiny, emerald green beetle from the jewel beetles family. In the Czech Republic, it is a critically endangered species, which unfortunately only occurs in a few places. Its required habitat for its short four-year life is the sunlit wood of old large oaks. The problem is that our forest stands are too dense and therefore shaded for the carp, and it does not use them with rare exceptions.
Tree microhabitats associated with me
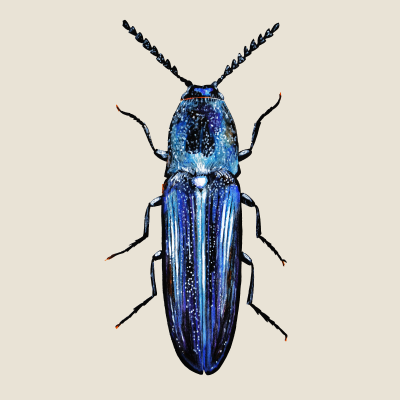

Violet click beetle
(Limoniscus violaceus)Violet click beetle (Limoniscus violaceus)
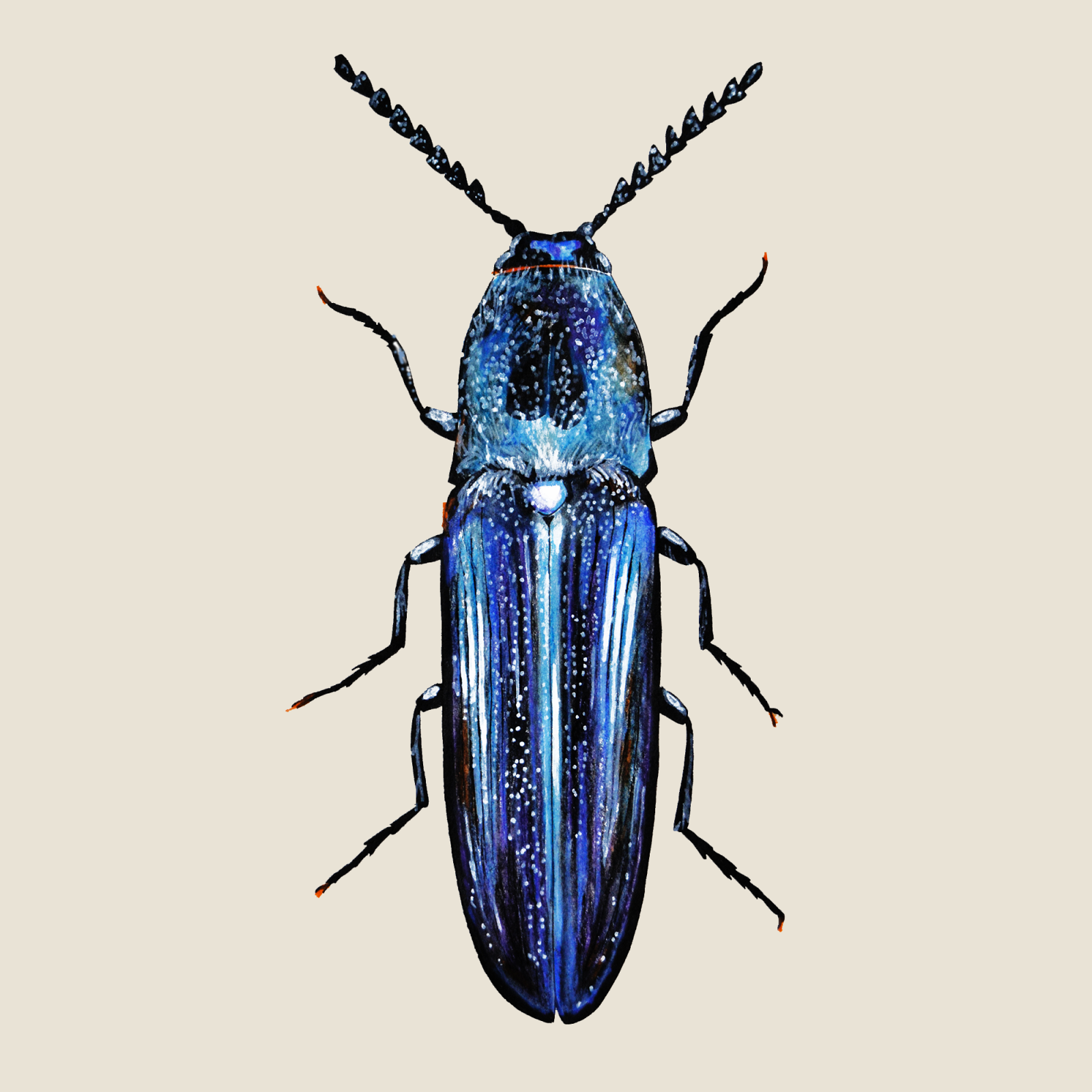

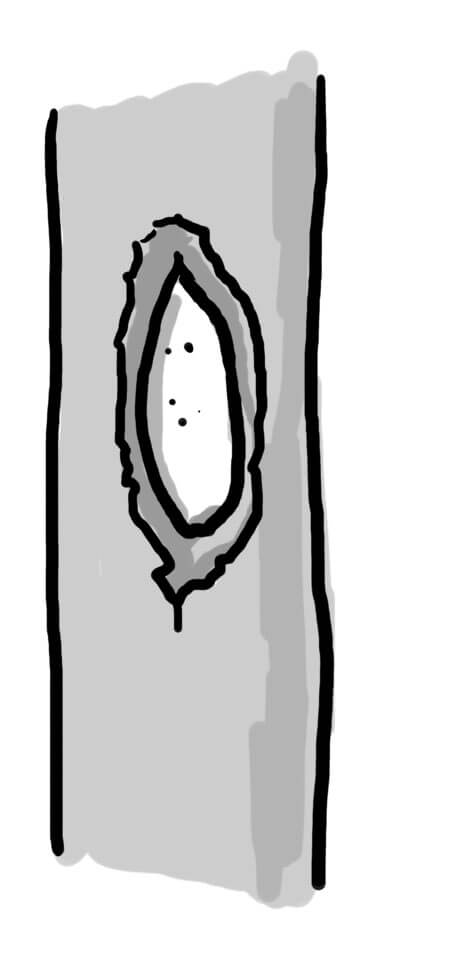
The Violet Click Beetle is a pan-European endangered black beetle with a faint blue-violet sheen. It is strictly bound to the original deciduous forests. It requires a number of hollow trees with a suitable microclimate and advanced decomposition, ideally at the base of the trunk in contact with the soil. The larva feeds on dead insects, but also actively hunts. Adults rarely leave the cavity.
Tree microhabitats associated with me
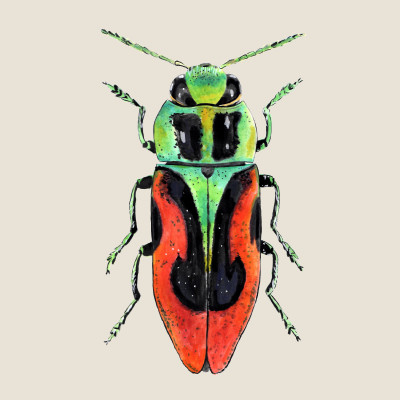

Cherry Jewel Beetle
(Anthaxia candens)Cherry Jewel Beetle (Anthaxia candens)
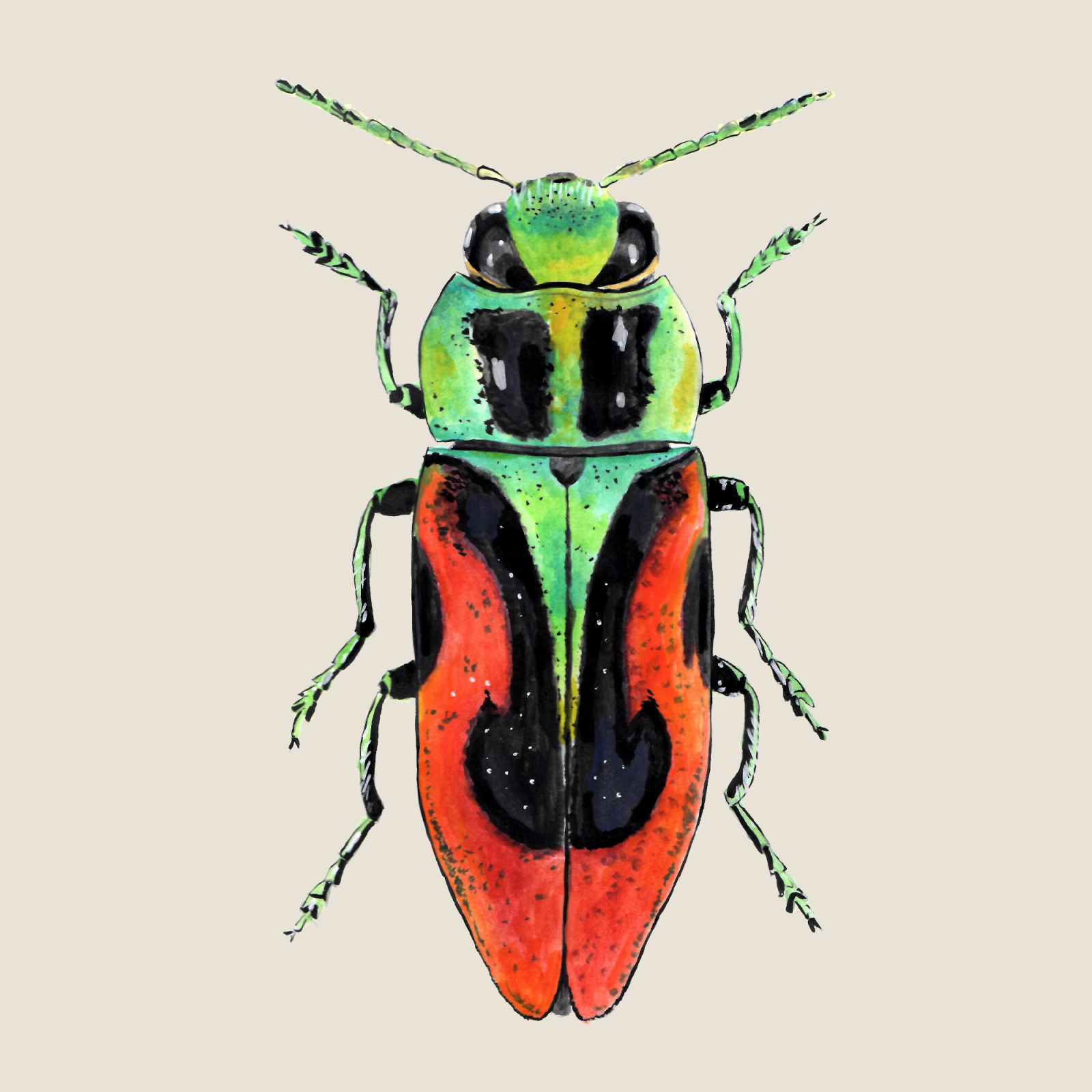

The cherry Jewel Beetle is a striking, brightly colored species from the jewel beetles family. Its main nutrient tree in the conditions of the Czech Republic is cherry (Prunus avium). It prefers drought-loving and heat-loving sunny habitats of old extensive cherry orchards and road alleys.
Tree microhabitats associated with me
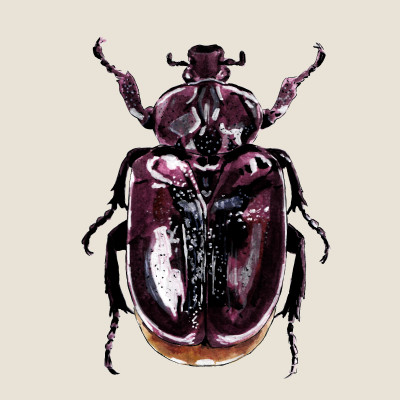

Hermit beetle
(Osmoderma barnabita)Hermit beetle (Osmoderma barnabita)
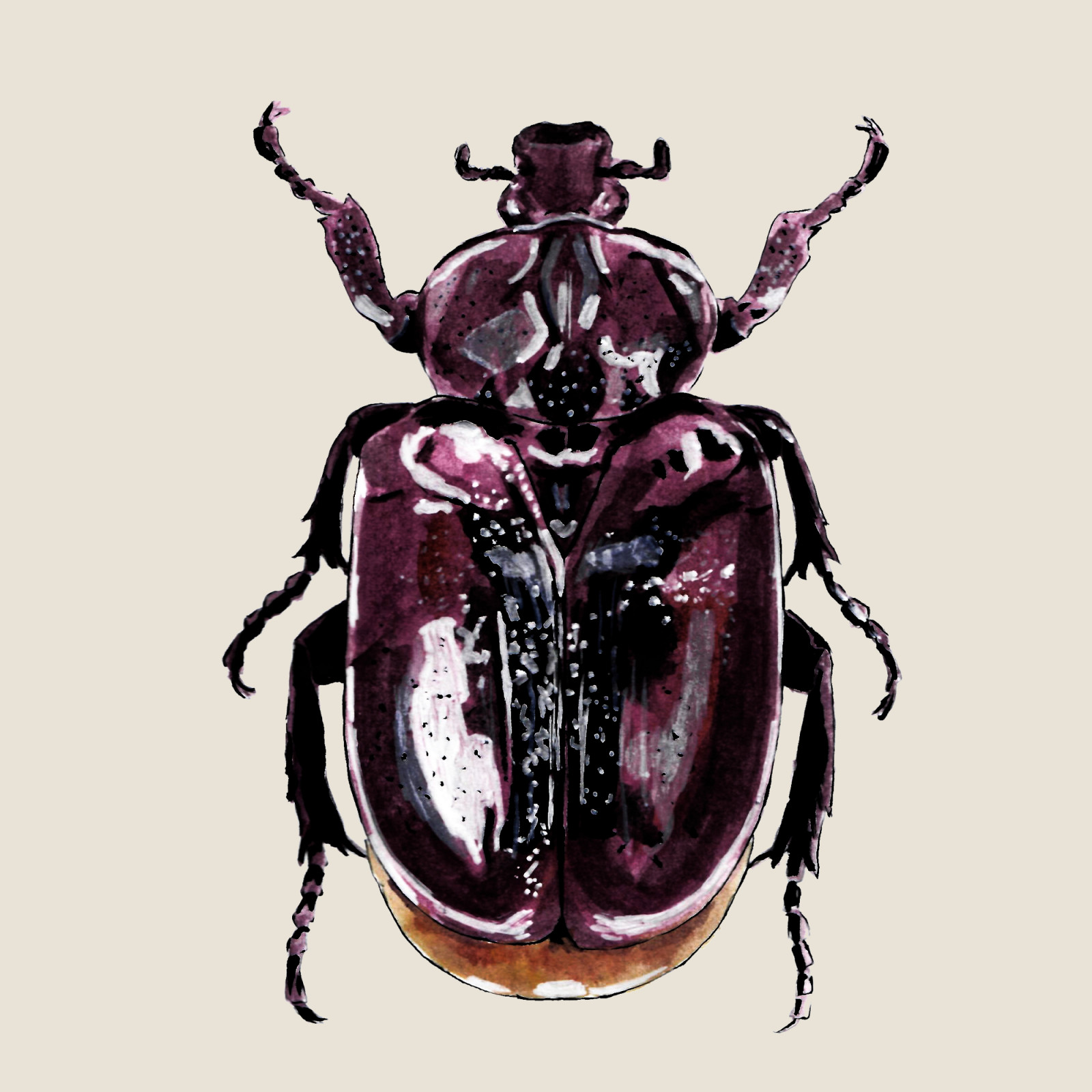

The Hermit Beetle is a species of scarab beetle in the family Scarabaeidae. Larvae of the hermit beetle develop in the hollows of old deciduous trees. Adults emit a characteristic smell, which also gave them their name. Hermit beetle can only fly short distances, and it is typical for them to form micropopulations that are prone to extinction in the event of a lack of suitable habitats.
Tree microhabitats associated with me
Code: 5
Trunk base rot-hole (closed top, ground contact)
Type
Opening ø > 10 cm
Description
Cavity chamber is completely protected from surrounding microclimate and rain Top-closed trunk cavity containing more or less mould (depending on its development stage). The cavity bottom has ground contact. Note that the cavity entrance can be higher on the trunk. Countable.
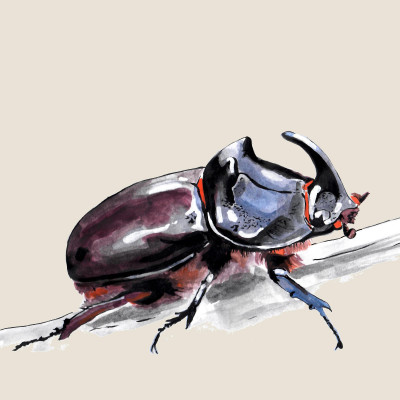

European rhinoceros beetle
(Oryctes nasicornis)European rhinoceros beetle (Oryctes nasicornis)
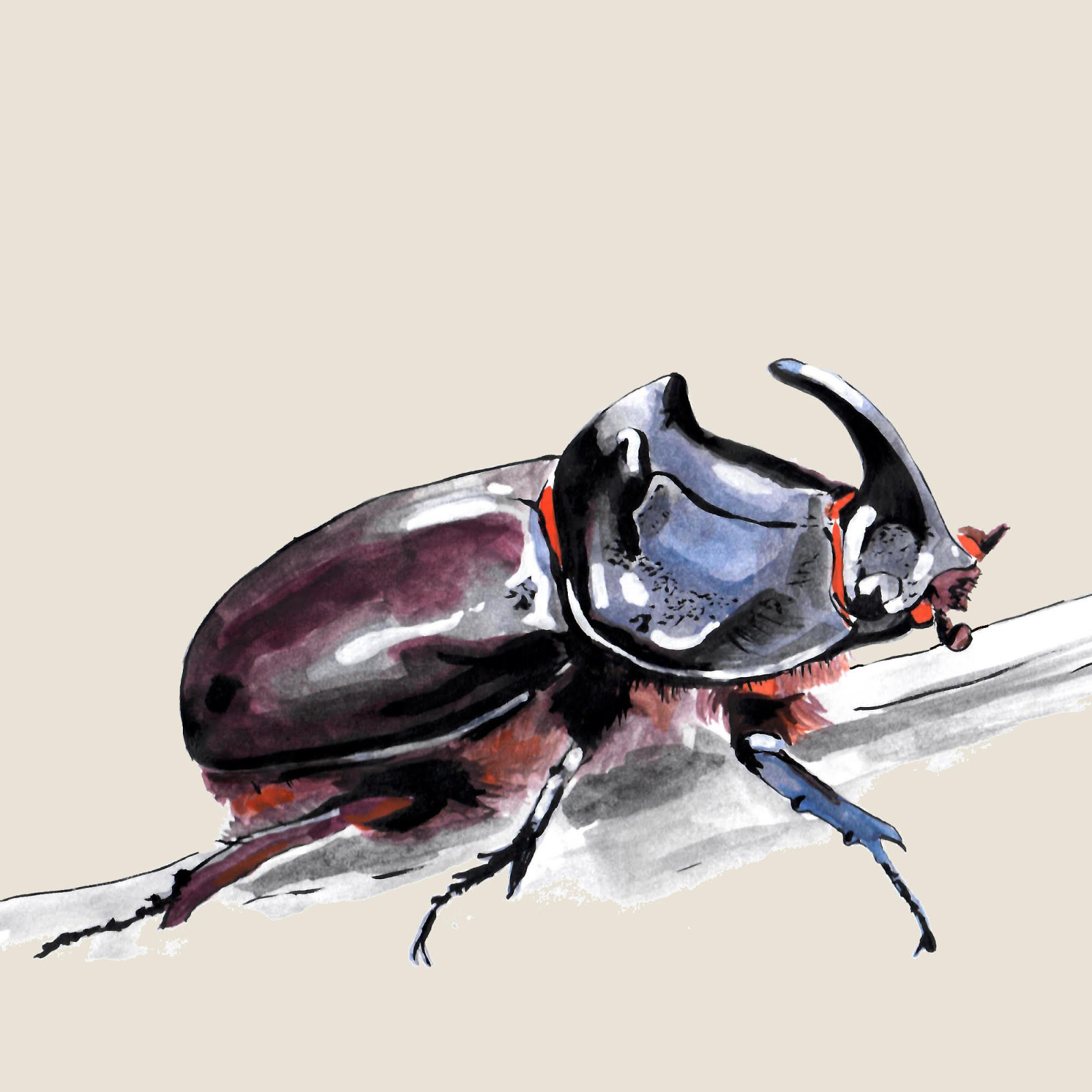

The European Rhinoceros Beetle is a relatively large beetle belonging to the subfamily Dynastinae. The dominant feature of males is a horn of varying length on the head and a raised shield, while females have only a small bump instead of a horn. Larvae develop in rotting wood of deciduous trees, but also in compost or piles of sawdust. Adults are active especially in the evening and at night and feed on sap
Tree microhabitats associated with me
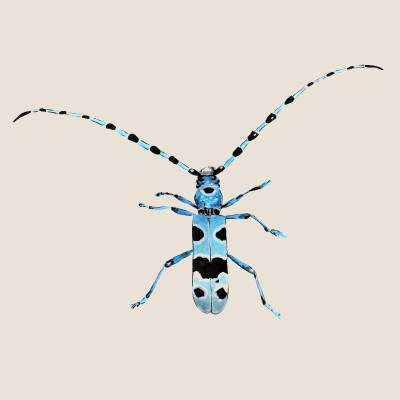
Rosalia longicorn
(Rosalia alpina)Rosalia longicorn (Rosalia alpina)
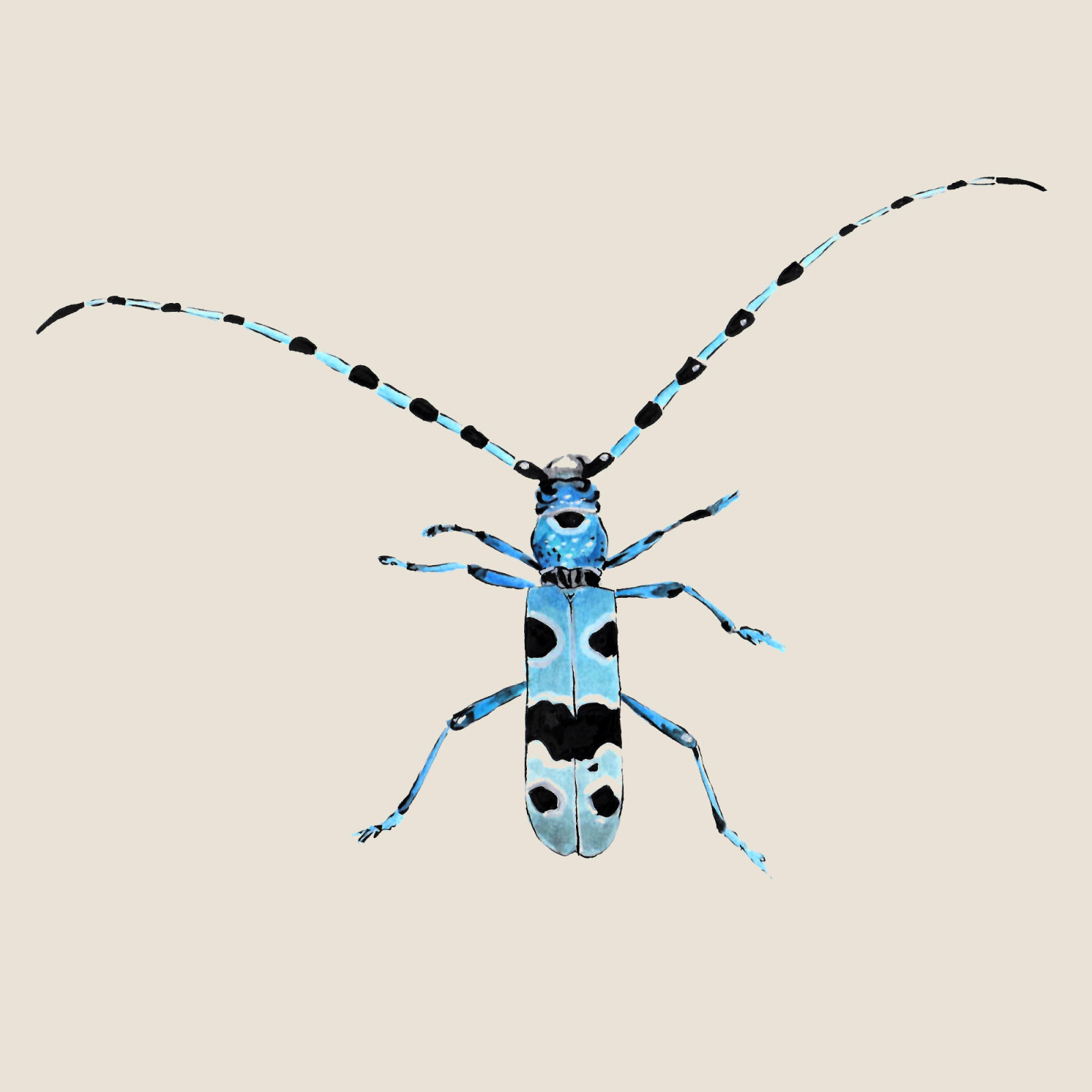
The Rosalia Longicorn is a species of large beetle in the longcorns family. The most numerous populations are associated with primary forest stands with freshly dead or dying beech trees. Adults usually prefer southern, warm slopes and feed on the sap of wounded trees.
Tree microhabitats associated with me
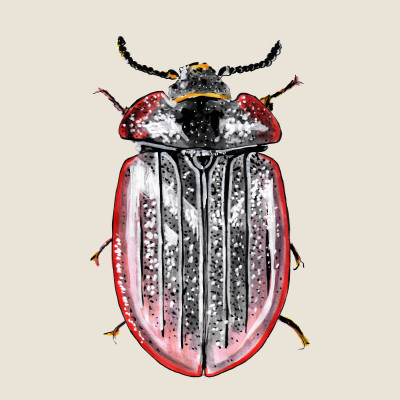

Peltis grossa
(Peltis grossa)Peltis grossa (Peltis grossa)
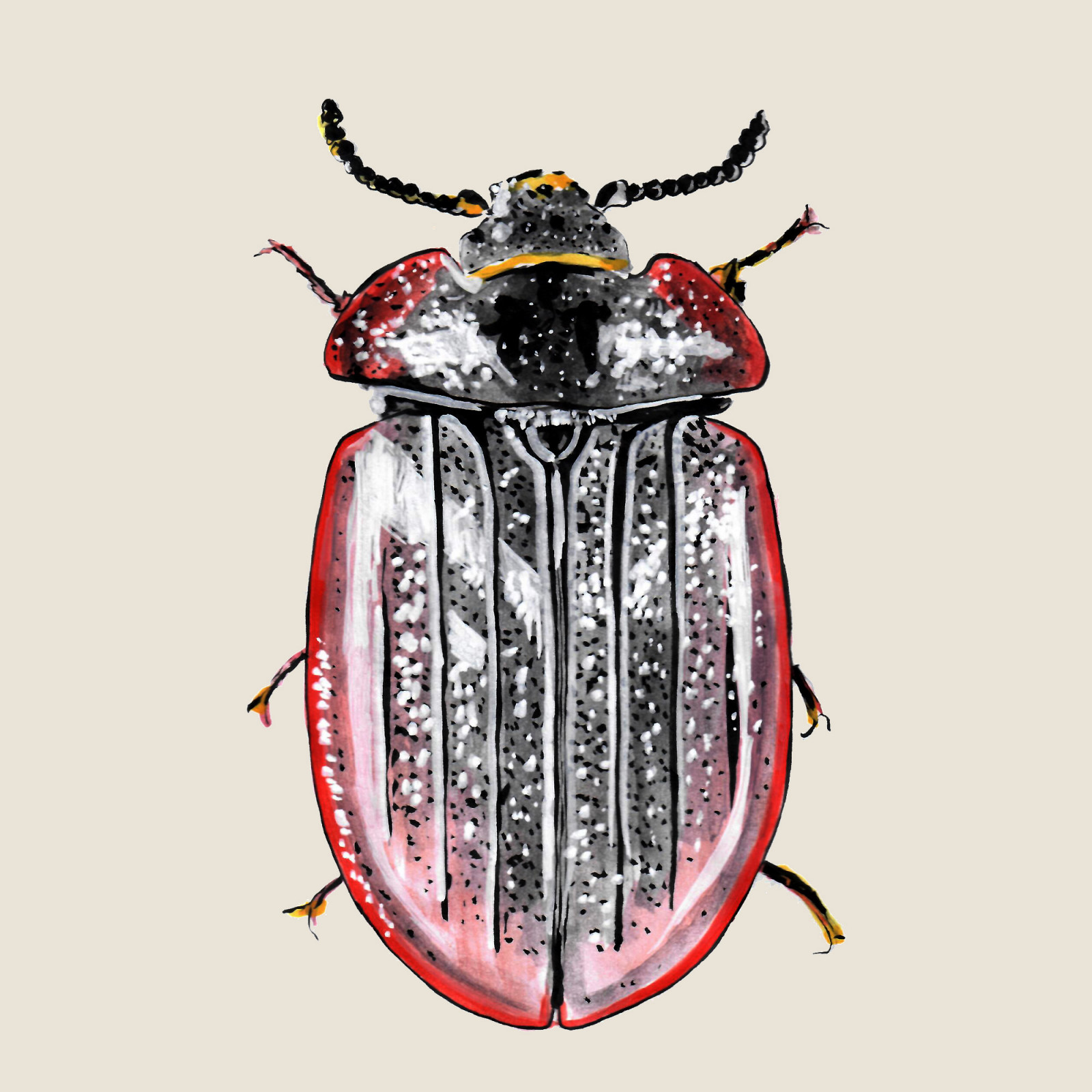

Peltis grossa is the largest representative of the Trogossitidae family with black or black-brown coloring. The beetle mainly inhabits well-preserved primary forests. Adults and larvae mainly prefer dead standing conifers attacked by fungi (especially the Red-banded Polypore). Larvae live in rotting wood, while adults prefer loose or exfoliated bark.
Tree microhabitats associated with me
Pick a pair

Hoof fungus
(Fomes fomentarius)

Red fox
(Vulpes vulpes)

Stock dove
(Columba oenas)

Goat moth
(Cossus cossus)

Hermit beetle
(Osmoderma barnabita)
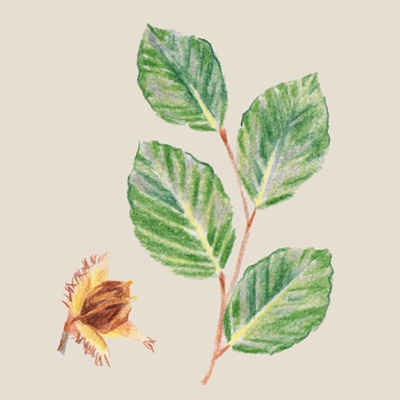

Beech
(Fagus)

Hoof fungus
(Fomes fomentarius)

Red fox
(Vulpes vulpes)

Grey-headed Woodpecker
(Picus canus)

Larch
(Larix)

White-backed woodpecker
(Dendrocopos leucotos)

Grey-headed Woodpecker
(Picus canus)

European badger
(Meles meles)

Stock dove
(Columba oenas)

Larch
(Larix)

Goat moth
(Cossus cossus)

Beard moss
(Usnea barbata)

White-backed woodpecker
(Dendrocopos leucotos)

European badger
(Meles meles)

Tawny owl
(Strix aluco)

Beard moss
(Usnea barbata)

Tawny owl
(Strix aluco)

Hermit beetle
(Osmoderma barnabita)

Beech
(Fagus)
Done
Do you want to play again?